My PhD Thesis, PDF 3MB - Stanford University
My PhD Thesis, PDF 3MB - Stanford University
My PhD Thesis, PDF 3MB - Stanford University
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
of the complicated geometrical spreading, we have difficulty to used the frequency shift<br />
method calculating attenuation logs for boreholes with invaded zones.<br />
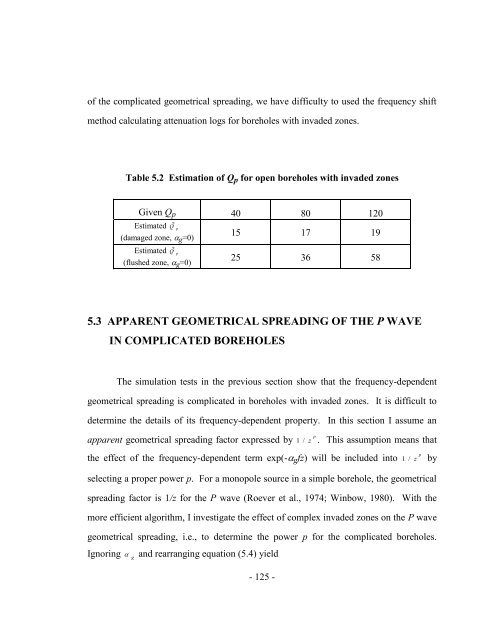
Table 5.2 Estimation of Qp for open boreholes with invaded zones<br />
Given Qp 40 80 120<br />
Estimated ?<br />
Q p<br />
(damaged zone, g=0)<br />
Estimated ?<br />
Q p<br />
(flushed zone, g=0)<br />
15 17 19<br />
25 36 58<br />
5.3 APPARENT GEOMETRICAL SPREADING OF THE P WAVE<br />
IN COMPLICATED BOREHOLES<br />
The simulation tests in the previous section show that the frequency-dependent<br />
geometrical spreading is complicated in boreholes with invaded zones. It is difficult to<br />
determine the details of its frequency-dependent property. In this section I assume an<br />
apparent geometrical spreading factor expressed by 1 / z p<br />
. This assumption means that<br />
the effect of the frequency-dependent term exp(-gfz) will be included into 1 / z p<br />
selecting a proper power p. For a monopole source in a simple borehole, the geometrical<br />
spreading factor is 1/z for the P wave (Roever et al., 1974; Winbow, 1980). With the<br />
more efficient algorithm, I investigate the effect of complex invaded zones on the P wave<br />
geometrical spreading, i.e., to determine the power p for the complicated boreholes.<br />
Ignoring g and rearranging equation (5.4) yield<br />
- 125 -<br />
by