Pavement Structural Analysis of the Design Recommendations for ...
Pavement Structural Analysis of the Design Recommendations for ...
Pavement Structural Analysis of the Design Recommendations for ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Pavement</strong> <strong>Structural</strong> <strong>Analysis</strong> August 2004<br />
Report No. 15953-2/1 ARA-ERES Consultants<br />
Number <strong>of</strong> Monthly Tridem Axle Loads<br />
3500<br />
3000<br />
2500<br />
2000<br />
1500<br />
1000<br />
500<br />
0<br />
0 20 40 60 80 100 120<br />
Tridem Axle Load, kips<br />
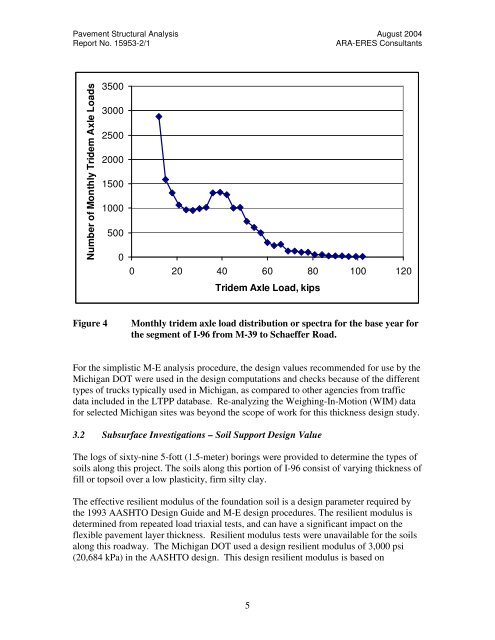
Figure 4 Monthly tridem axle load distribution or spectra <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> base year <strong>for</strong><br />
<strong>the</strong> segment <strong>of</strong> I-96 from M-39 to Schaeffer Road.<br />
For <strong>the</strong> simplistic M-E analysis procedure, <strong>the</strong> design values recommended <strong>for</strong> use by <strong>the</strong><br />
Michigan DOT were used in <strong>the</strong> design computations and checks because <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> different<br />
types <strong>of</strong> trucks typically used in Michigan, as compared to o<strong>the</strong>r agencies from traffic<br />
data included in <strong>the</strong> LTPP database. Re-analyzing <strong>the</strong> Weighing-In-Motion (WIM) data<br />
<strong>for</strong> selected Michigan sites was beyond <strong>the</strong> scope <strong>of</strong> work <strong>for</strong> this thickness design study.<br />
3.2 Subsurface Investigations – Soil Support <strong>Design</strong> Value<br />
The logs <strong>of</strong> sixty-nine 5-fott (1.5-meter) borings were provided to determine <strong>the</strong> types <strong>of</strong><br />
soils along this project. The soils along this portion <strong>of</strong> I-96 consist <strong>of</strong> varying thickness <strong>of</strong><br />
fill or topsoil over a low plasticity, firm silty clay.<br />
The effective resilient modulus <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> foundation soil is a design parameter required by<br />
<strong>the</strong> 1993 AASHTO <strong>Design</strong> Guide and M-E design procedures. The resilient modulus is<br />
determined from repeated load triaxial tests, and can have a significant impact on <strong>the</strong><br />
flexible pavement layer thickness. Resilient modulus tests were unavailable <strong>for</strong> <strong>the</strong> soils<br />
along this roadway. The Michigan DOT used a design resilient modulus <strong>of</strong> 3,000 psi<br />
(20,684 kPa) in <strong>the</strong> AASHTO design. This design resilient modulus is based on<br />
5