Utility of History, Physical Examination, Electrocardiogram, and ...
Utility of History, Physical Examination, Electrocardiogram, and ...
Utility of History, Physical Examination, Electrocardiogram, and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
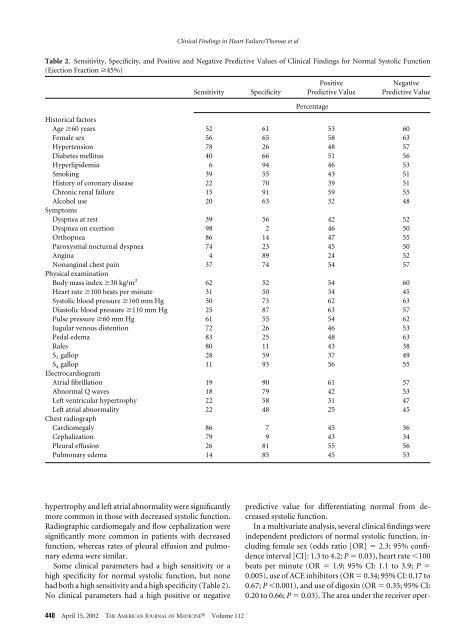
Table 2. Sensitivity, Specificity, <strong>and</strong> Positive <strong>and</strong> Negative Predictive Values <strong>of</strong> Clinical Findings for Normal Systolic Function<br />
(Ejection Fraction 45%)<br />
hypertrophy <strong>and</strong> left atrial abnormality were significantly<br />
more common in those with decreased systolic function.<br />
Radiographic cardiomegaly <strong>and</strong> flow cephalization were<br />
significantly more common in patients with decreased<br />
function, whereas rates <strong>of</strong> pleural effusion <strong>and</strong> pulmonary<br />
edema were similar.<br />
Some clinical parameters had a high sensitivity or a<br />
high specificity for normal systolic function, but none<br />
had both a high sensitivity <strong>and</strong> a high specificity (Table 2).<br />
No clinical parameters had a high positive or negative<br />
Clinical Findings in Heart Failure/Thomas et al<br />
Sensitivity Specificity<br />
Positive<br />
Predictive Value<br />
Negative<br />
Predictive Value<br />
Percentage<br />
Historical factors<br />
Age 60 years 52 61 53 60<br />
Female sex 56 65 58 63<br />
Hypertension 78 26 48 57<br />
Diabetes mellitus 40 66 51 56<br />
Hyperlipidemia 6 94 46 53<br />
Smoking 39 55 43 51<br />
<strong>History</strong> <strong>of</strong> coronary disease 22 70 39 51<br />
Chronic renal failure 15 91 59 55<br />
Alcohol use<br />
Symptoms<br />
20 63 32 48<br />
Dyspnea at rest 39 56 42 52<br />
Dyspnea on exertion 98 2 46 50<br />
Orthopnea 86 14 47 55<br />
Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea 74 23 45 50<br />
Angina 4 89 24 52<br />
Nonanginal chest pain<br />
<strong>Physical</strong> examination<br />
37 74 54 57<br />
Body mass index 30 kg/m 2<br />
62 52 54 60<br />
Heart rate 100 beats per minute 31 50 34 45<br />
Systolic blood pressure 160 mm Hg 50 73 62 63<br />
Diastolic blood pressure 110 mm Hg 25 87 63 57<br />
Pulse pressure 60 mm Hg 61 55 54 62<br />
Jugular venous distention 72 26 46 53<br />
Pedal edema 83 25 48 63<br />
Rales 80 11 43 38<br />
S3 gallop 28 59 37 49<br />
S4 gallop<br />
<strong>Electrocardiogram</strong><br />
11 93 56 55<br />
Atrial fibrillation 19 90 61 57<br />
Abnormal Q waves 18 79 42 53<br />
Left ventricular hypertrophy 22 58 31 47<br />
Left atrial abnormality<br />
Chest radiograph<br />
22 48 25 45<br />
Cardiomegaly 86 7 45 36<br />
Cephalization 79 9 43 34<br />
Pleural effusion 26 81 55 56<br />
Pulmonary edema 14 85 45 53<br />
440 April 15, 2002 THE AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE Volume 112<br />
predictive value for differentiating normal from decreased<br />
systolic function.<br />
In a multivariate analysis, several clinical findings were<br />
independent predictors <strong>of</strong> normal systolic function, including<br />
female sex (odds ratio [OR] 2.3; 95% confidence<br />
interval [CI]: 1.3 to 4.2; P 0.03), heart rate 100<br />
beats per minute (OR 1.9; 95% CI: 1.1 to 3.9; P <br />
0.005), use <strong>of</strong> ACE inhibitors (OR 0.34; 95% CI: 0.17 to<br />
0.67; P 0.001), <strong>and</strong> use <strong>of</strong> digoxin (OR 0.35; 95% CI:<br />
0.20 to 0.66; P 0.03). The area under the receiver oper-