Gugrajah_Yuvaan_ Ramesh_2003.pdf
Gugrajah_Yuvaan_ Ramesh_2003.pdf
Gugrajah_Yuvaan_ Ramesh_2003.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Adaptation ofthe Fixed Point Approximation to Ad Hoc Networks<br />
Chapter 5<br />
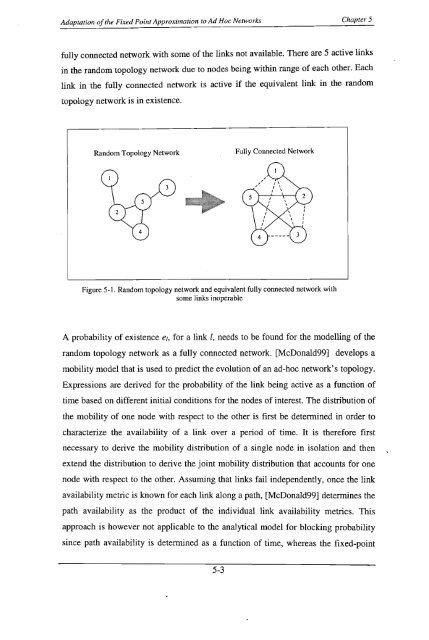
fully connected network with some of the links not available. There are 5 active links<br />
in the random topology network due to nodes being within range of each other. Each<br />
link in the fully connected network is active if the equivalent link in the random<br />
topology network is in existence.<br />
Random Topology Network<br />
Fully Connected Network<br />
Figure 5-1. Random topology network and equivalent fully connected network with<br />
some links inoperable<br />
A probability of existence et, for a link t, needs to be found for the modelling of the<br />
random topology network as a fully connected network. [McDonald99] develops a<br />
mobility model that is used to predict the evolution of an ad-hoc network's topology.<br />
Expressions are derived for the probability of the link being active as a function of<br />
time based on different initial conditions for the nodes of interest. The distribution of<br />
the mobility of one node with respect to the other is first be determined in order to<br />
characterize the availability of a link over a period of time. It is therefore first<br />
necessary to derive the mobility distribution of a single node in isolation and then<br />
extend the distribution to derive the joint mobility distribution that accounts for one<br />
node with respect to the other. Assuming that links fail independently, once the link<br />
availability metric is known for each link along a path, [McDonald99] determines the<br />
path availability as the product of the individual link availability metrics. This<br />
approach is however not applicable to the analytical model for blocking probability<br />
since path availability is determined as a function of time, whereas the fixed-point<br />
5-3