EtherCAT Slave Implementation Guide
EtherCAT Slave Implementation Guide
EtherCAT Slave Implementation Guide
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
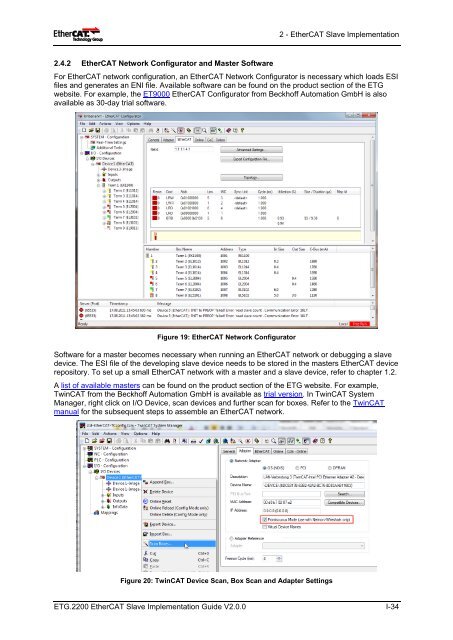
2.4.2 <strong>EtherCAT</strong> Network Configurator and Master Software<br />
2 - <strong>EtherCAT</strong> <strong>Slave</strong> <strong>Implementation</strong><br />
For <strong>EtherCAT</strong> network configuration, an <strong>EtherCAT</strong> Network Configurator is necessary which loads ESI<br />
files and generates an ENI file. Available software can be found on the product section of the ETG<br />
website. For example, the ET9000 <strong>EtherCAT</strong> Configurator from Beckhoff Automation GmbH is also<br />
available as 30-day trial software.<br />
Figure 19: <strong>EtherCAT</strong> Network Configurator<br />
Software for a master becomes necessary when running an <strong>EtherCAT</strong> network or debugging a slave<br />
device. The ESI file of the developing slave device needs to be stored in the masters <strong>EtherCAT</strong> device<br />
repository. To set up a small <strong>EtherCAT</strong> network with a master and a slave device, refer to chapter 1.2.<br />
A list of available masters can be found on the product section of the ETG website. For example,<br />
TwinCAT from the Beckhoff Automation GmbH is available as trial version. In TwinCAT System<br />
Manager, right click on I/O Device, scan devices and further scan for boxes. Refer to the TwinCAT<br />
manual for the subsequent steps to assemble an <strong>EtherCAT</strong> network.<br />
Figure 20: TwinCAT Device Scan, Box Scan and Adapter Settings<br />
ETG.2200 <strong>EtherCAT</strong> <strong>Slave</strong> <strong>Implementation</strong> <strong>Guide</strong> V2.0.0 I-34