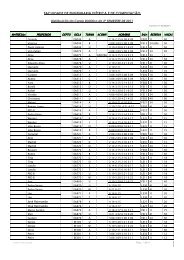
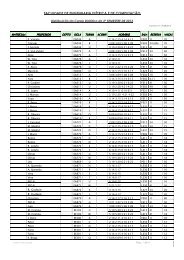
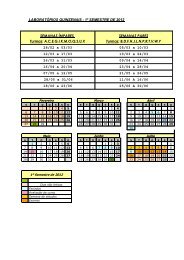
sinopseV3n3.pdf - FEEC - Unicamp
sinopseV3n3.pdf - FEEC - Unicamp
sinopseV3n3.pdf - FEEC - Unicamp
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Were selected models of learning, instructional project,<br />
production process and evaluation process. The infra-structure<br />
environment focus on open source and freeware tools, to meet<br />
market demand at competitive cost and enable greater<br />
geographical spread as possible.<br />
This work, was introduced, in a pioneer manner, perform<br />
experiments using computer simulations in a collaborative<br />
environment, changing the learning dynamics and creating a<br />
new interactive perspective between teacher and students in an<br />
effective environment for electronic e-learning. It was observed<br />
with this research a feasible way to teach remotely electronic<br />
with practical activities interactive and collaborative.<br />
Keywords: E-Learning, learning environment,<br />
electronics teaching, free software.<br />
Biomedical Engineering<br />
IDENTIFICATION OF INCONSISTENCIES AND<br />
INDETERMINACIES OF A MEDICAL EQUIPMENT<br />
CLASSIFICATION: PARACONSISTENT<br />
ANNOTATED LOGIC<br />
Identificação de inconsistências e<br />
indeterminações na classificação de<br />
equipamentos médico-hospitalares: lógica<br />
paraconsistente anotada<br />
Natália Ferreira Oshiyama<br />
Supervisor: José Wilson Magalhães Bassani<br />
(DEB/<strong>FEEC</strong>/UNICAMP)<br />
Defense date: Sep, 29 2010<br />
Abstract: Physicians have become dependent on medical<br />
equipment for safer and more efficient treatment of patients.<br />
Therefore, medical technology management has become more<br />
important. This work aimed at developing a methodology for<br />
classification of medical equipment based on the requirement of<br />
corrective maintenance, namely, frequency of failures, as well<br />
as time and cost of this kind of service. Equipment classes were<br />
established using the Always Better Control analysis (ABC).<br />
The paraconsistent annotated logic (PAL) was used to identify<br />
inconsistencies and indeterminacies that might arise from the<br />
equipment classification, pointing out to the clinical<br />
engineering team specific equipments that required a more<br />
detailed, post-hoc, case analysis. As almost 90% of the<br />
classifications did not present inconsistencies and/or<br />
indeterminacies, it is possible to conclude that the classification<br />
was coherent and may be used as a tool for helping clinical<br />
engineers on their daily management work, new equipment<br />
acquisition and replacement planning, data mining for<br />
equipment manufacturers and by regulatory agencies<br />
Keywords: medical equipment classification, ABC<br />
analysis, paraconsistent annotated logic, clinical<br />
engineering.<br />
Terapia elétrica funcional intensiva no membro<br />
superior parético de pacientes pós acidente<br />
vascular encefálico<br />
Fernanda Passos Dos Reis Ervilha<br />
Supervisor: José Wilson Magalhães Bassani<br />
(DEB/<strong>FEEC</strong>/UNICAMP)<br />
Defense date: Nov, 30 2010<br />
Abstract: Stroke often results with decreased ability to control<br />
shoulder and elbow movements, as well as compromised<br />
grasping. In the last decade, researchers have investigated the<br />
effect of simultaneously applied intensive neuromuscular<br />
electrical stimulation and functional exercises, aiming<br />
rehabilitation of hand movements. Once proved to be effective,<br />
Intensive Functional Electrical Therapy (IFET) tends to be<br />
widely used in rehabilitation centers due to decreased treatment<br />
time needed for each patient. The present study aimed to<br />
compare the effect of functional therapy with functional therapy<br />
plus IFET, in short, medium, and in a long term. Ten<br />
volunteers, with mean (±SD) age and EVA time 63.1 (±11) and<br />
7.9 (±6.8) weeks and months, respectively, were randomly<br />
selected and divided in two groups. . Eight volunteers<br />
concluded the study. Volunteers underwent to 5 weeks of<br />
treatment, composed of 30 minutes of conventional therapy in<br />
addition to 30 minutes of IFET. For the experimental group, a<br />
four channel electrical stimulator Actigrip® CS system was<br />
used. In the first two weeks of treatment using electrical<br />
stimulation, only upper limb proximal muscles were stimulated<br />
(m. deltoid – anterior and lateral fibers), with surface<br />
electrodes, using a 200 ìs, 50 Hz, compensated monophasic<br />
pulse, 20-45 mA of intensity. Motor function was evaluated<br />
using the Upper Extremity Functioning Test -UEFT), Drawing<br />
Test- DT, and neurological evaluation. Analysis of variance<br />
(ANOVA) showed significant difference (F(4, 20)=8, 4; p<0,<br />
01) for the parameter number of functional task repetitions. The<br />
Tukey Honest Significant Difference test showed that both,<br />
TEFI and control groups significantly increased the number of<br />
motor task repetitions they could perform in two<br />
minutes(p<0, 03). This was significant when pre-treatment<br />
was compared with post-treatment (2 and 5 weeks of treatment,<br />
and 12 and 24 weeks of follow-up). The number of times the<br />
volunteers performed the motor task increased from 8 to<br />
approximately 11. In conclusion, functional training of upper<br />
limb, impaired due to stroke, whether added or not to intensive<br />
electrical stimulation improved motor function. This result was<br />
obtained after two weeks of treatment and last for a period of<br />
24 weeks.<br />
Keywords: stroke, intensive functional electrical<br />
therapy, upper extremity paresis, neuromuscular<br />
electrical stimulation, rehabilitation, functional training,<br />
grasping, physiotherapy.<br />
HYPERMEDIA SYSTEM FOR SUPPORT IN<br />
TECHNICAL TEACHING OF MEDICAL<br />
EQUIPMENT<br />
Sistema hipermídia para apoio ao ensino técnico<br />
de equipamentos médico-hospitalares<br />
Debora Dias Leister Batista<br />
Supervisor: Sérgio Santos Muhlen (DEB/<strong>FEEC</strong>/UNICAMP)<br />
Defense date: Dec, 02 2010<br />
Abstract: This study presents the construction and evaluation<br />
of a hypermedia system to facilitate technical teaching of<br />
medical-hospital equipment, in a technician preparation course<br />
supported by an industrial institution, aiming to contribute for<br />
the teach-learning process. In this first version, the hypermedia<br />
system is focused in one equipment (cardiac defibrillator). It<br />
was evaluated by a selected group of students, having passed a<br />
pre-test to determine their previous knowledge on the matter,<br />
then using the system proposed, and a post-test to evaluate the<br />
gain. The results showed the learning level was significantly<br />
greater among students that used the hipermedia system,<br />
confirming its value for the teaching-learning process.<br />
Keywords: technical teaching, teach-learning,<br />
Hypermedia, defibrillator.<br />
Computer Engineering<br />
A STUDY ABOUT IMPLEMENTATION OF<br />
ELLIPTIC CURVE PAIRING BASED<br />
CRYPTOSYSTEMS IN 8-BIT SMART CARDS<br />
Um estudo sobre a implementação de<br />
criptossistemas baseados em emparelhamentos<br />
bilineares sobre curvas elípticas em cartões<br />
inteligentes de oito bits<br />
Matheus Fernandes De Oliveira<br />
Supervisor: Marco Aurélio Amaral Henriques<br />
(DCA/<strong>FEEC</strong>/UNICAMP)<br />
Defense date: Oct, 01 2010<br />
Abstract: Bilinear pairings over elliptic curves are<br />
mathematical functions that enable the development of a set of<br />
92 Sinopse da <strong>FEEC</strong>