Multiplier
Multiplier
Multiplier
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
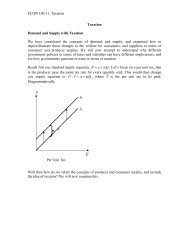
Introduction to Economics, ECON 100:11 & 13<br />
<strong>Multiplier</strong> Model<br />
C,I,G,S,T.<br />
Aggregate<br />
Demand<br />
AE=Y, 45 o line<br />
( c dY )<br />
X − IM = X − +<br />
Real<br />
Income<br />
4. Since we know that aggregate expenditure is the sum of all these above elements<br />
from point 1 to 3. To depict the relationship, all we need is to perform vertical<br />
summation. Why? First, let us sum autonomous G, and I to consumption C.<br />
C,I,G,S,T.<br />
Aggregate<br />
Demand<br />
AE=Y, 45 o line<br />
C + I 0<br />
+ G 0<br />
C + I 0<br />
C<br />
I = I 0<br />
G = G 0<br />
Real<br />
Income<br />
To include net exports, simply do the same. However, note that<br />
X − IM = X − ( c + dY ) is downward sloping with respect to real income, since as<br />
income rises the marginal propensity to import rises. This means that the slope of<br />
the AE line is gentler. What is the slope of the AE curve?<br />
4







![The Rink - Cyril Dabydeen[1].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/21946808/1/155x260/the-rink-cyril-dabydeen1pdf.jpg?quality=85)







