Stall warnings in high capacity aircraft: The Australian context 2008 ...
Stall warnings in high capacity aircraft: The Australian context 2008 ...
Stall warnings in high capacity aircraft: The Australian context 2008 ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
ATSB – AR-2012-172<br />
What conditions were <strong>aircraft</strong> <strong>in</strong> when the stall warn<strong>in</strong>g occurred?<br />
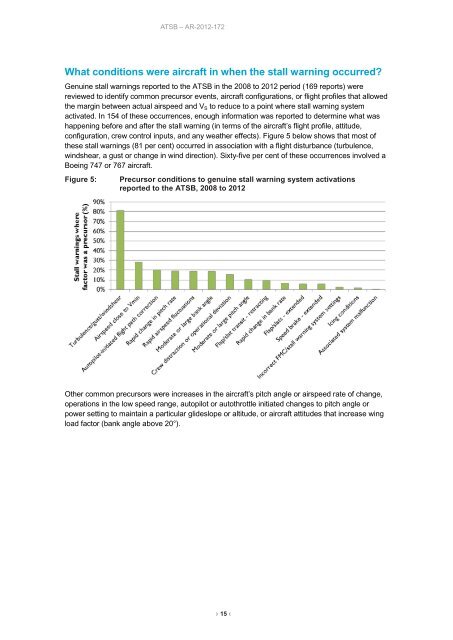
Genu<strong>in</strong>e stall <strong>warn<strong>in</strong>gs</strong> reported to the ATSB <strong>in</strong> the <strong>2008</strong> to 2012 period (169 reports) were<br />
reviewed to identify common precursor events, <strong>aircraft</strong> configurations, or flight profiles that allowed<br />
the marg<strong>in</strong> between actual airspeed and V S to reduce to a po<strong>in</strong>t where stall warn<strong>in</strong>g system<br />
activated. In 154 of these occurrences, enough <strong>in</strong>formation was reported to determ<strong>in</strong>e what was<br />
happen<strong>in</strong>g before and after the stall warn<strong>in</strong>g (<strong>in</strong> terms of the <strong>aircraft</strong>’s flight profile, attitude,<br />
configuration, crew control <strong>in</strong>puts, and any weather effects). Figure 5 below shows that most of<br />
these stall <strong>warn<strong>in</strong>gs</strong> (81 per cent) occurred <strong>in</strong> association with a flight disturbance (turbulence,<br />
w<strong>in</strong>dshear, a gust or change <strong>in</strong> w<strong>in</strong>d direction). Sixty-five per cent of these occurrences <strong>in</strong>volved a<br />
Boe<strong>in</strong>g 747 or 767 <strong>aircraft</strong>.<br />
Figure 5:<br />
Precursor conditions to genu<strong>in</strong>e stall warn<strong>in</strong>g system activations<br />
reported to the ATSB, <strong>2008</strong> to 2012<br />
Other common precursors were <strong>in</strong>creases <strong>in</strong> the <strong>aircraft</strong>’s pitch angle or airspeed rate of change,<br />
operations <strong>in</strong> the low speed range, autopilot or autothrottle <strong>in</strong>itiated changes to pitch angle or<br />
power sett<strong>in</strong>g to ma<strong>in</strong>ta<strong>in</strong> a particular glideslope or altitude, or <strong>aircraft</strong> attitudes that <strong>in</strong>crease w<strong>in</strong>g<br />
load factor (bank angle above 20°).<br />
› 15 ‹