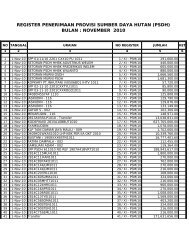
BERAU HERBARIUM
BERAU HERBARIUM
BERAU HERBARIUM
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Family<br />
Genus<br />
Species<br />
Vernacular name with the name of the dialect or language<br />
Local uses<br />
Collector Prefix<br />
Number<br />
Location (Country/ Province/ Administrative region/ Town/village<br />
Longitude and latitude<br />
Altitude<br />
Habitat<br />
Habit – this includes include notes on overall form of the plants, height, diameter,<br />
bark, buttresses, wood, colour of flowers and fruits; essentially those characters that<br />
will be not be available on specimens<br />
Like number tags, pencil should be used for writing in field books, as it will not wash off.<br />
Selecting the specimens<br />
When plants are small and fit to the size of the mounting paper one should dig out the whole<br />
plant and dry the specimens including a portion of the root system. When plants are woody<br />
or too large to make an entire specimen, usually only fertile clippings will be taken. Fertile<br />
clippings are branches with flowers or fruits (preferably both). Generally, at least seven<br />
duplicates are collected. Number tags are attached and the material stored temporarily in<br />
large polythene bags to avoid the specimens drying out before they can be properly<br />
processed.<br />
Large trees should be climbed to reach the fertile branches (figure 7). Safety regulations<br />
must be followed. At minimum, two trained climbers should be involved in the collecting<br />
activities.<br />
7