(HCVF) Toolkit for Malaysia - HCV Resource Network
(HCVF) Toolkit for Malaysia - HCV Resource Network
(HCVF) Toolkit for Malaysia - HCV Resource Network
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5) What is the long-term viability of the local populations of these species?<br />
When you have carried out surveys of the key endangered species in your FMU you will have quantitative<br />
data that can be used to estimate their abundance in your FMU. As a rule, to prevent genetic inbreeding,<br />
at least 50 breeding animals are needed to make up a viable population. The space needed by 50<br />
breeding mice is very different from that of 50 breeding tigers. As a guide, larger animals generally require<br />
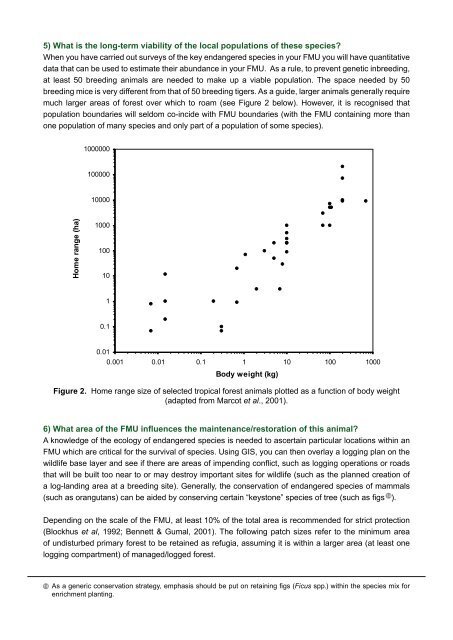
much larger areas of <strong>for</strong>est over which to roam (see Figure 2 below). However, it is recognised that<br />
population boundaries will seldom co-incide with FMU boundaries (with the FMU containing more than<br />
one population of many species and only part of a population of some species).<br />
Figure 2. Home range size of selected tropical <strong>for</strong>est animals plotted as a function of body weight<br />
(adapted from Marcot et al., 2001).<br />
6) What area of the FMU influences the maintenance/restoration of this animal?<br />
A knowledge of the ecology of endangered species is needed to ascertain particular locations within an<br />
FMU which are critical <strong>for</strong> the survival of species. Using GIS, you can then overlay a logging plan on the<br />
wildlife base layer and see if there are areas of impending conflict, such as logging operations or roads<br />
that will be built too near to or may destroy important sites <strong>for</strong> wildlife (such as the planned creation of<br />
a log-landing area at a breeding site). Generally, the conservation of endangered species of mammals<br />
14<br />
(such as orangutans) can be aided by conserving certain “keystone” species of tree (such as figs ).<br />
Depending on the scale of the FMU, at least 10% of the total area is recommended <strong>for</strong> strict protection<br />
(Blockhus et al, 1992; Bennett & Gumal, 2001). The following patch sizes refer to the minimum area<br />
of undisturbed primary <strong>for</strong>est to be retained as refugia, assuming it is within a larger area (at least one<br />
logging compartment) of managed/logged <strong>for</strong>est.<br />
14 As a generic conservation strategy, emphasis should be put on retaining figs (Ficus spp.) within the species mix <strong>for</strong><br />
enrichment planting.