The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and ...
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and ...
The Finite Element Method for the Analysis of Non-Linear and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>The</strong> first two analysis types, although significantly simplified, can lead to valuable conclusions<br />
concerning <strong>the</strong> behavior <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> structure <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> possible collapse mechanism. <strong>The</strong> applied procedure<br />
can be described in brief as follows. In <strong>the</strong> case <strong>of</strong> 2-D analysis <strong>the</strong> structure is assumed to consist <strong>of</strong> a<br />
finite number <strong>of</strong> nodes interconnected by a finite number <strong>of</strong> elements. <strong>The</strong> types <strong>of</strong> elements have<br />
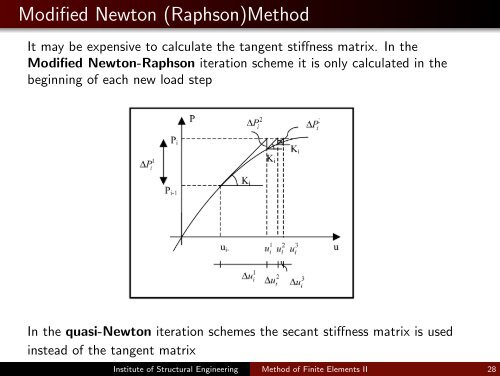
been It may described expensive in section 3. toIn calculate <strong>the</strong> case <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> 3-D tangent analysis <strong>the</strong> stiffness structure matrix. is assumed Into <strong>the</strong> consist <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong><br />
a<strong>for</strong>ementioned Modified Newton-Raphson 2-D frames, assuming a rigid iteration diaphragm scheme assemblage it is <strong>of</strong> only <strong>the</strong>ir calculated horizontal d<strong>of</strong>’s in <strong>the</strong> per floor<br />
slab. Loads may be applied at <strong>the</strong> nodes or along <strong>the</strong> elements. In both cases though, <strong>the</strong>y are<br />
trans<strong>for</strong>med beginning to nodal <strong>of</strong> each loads. new load step<br />
Modified Newton (Raphson)<strong>Method</strong><br />
Figure 5. Modified Newton Raphson <strong>Method</strong><br />
In <strong>the</strong> quasi-Newton iteration schemes <strong>the</strong> secant stiffness matrix is used<br />
instead <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> tangent matrix<br />
After <strong>the</strong> <strong>for</strong>mation <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> stiffness matrix <strong>the</strong> equilibrium equations are solved by an efficient<br />
algorithm based on <strong>the</strong> Gaussian elimination method. <strong>The</strong> structure stiffness is stored in a b<strong>and</strong>ed <strong>for</strong>m<br />
Institute <strong>of</strong> Structural Engineering <strong>Method</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Finite</strong> <strong>Element</strong>s II 28