Glossary and Abbreviations - Unido
Glossary and Abbreviations - Unido
Glossary and Abbreviations - Unido
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
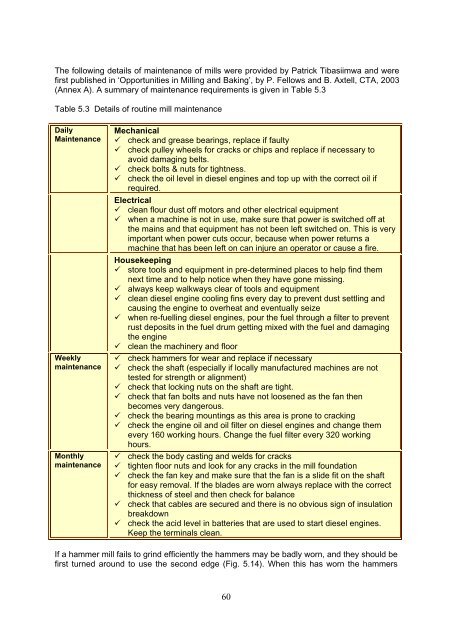
The following details of maintenance of mills were provided by Patrick Tibasiimwa <strong>and</strong> were<br />
first published in ‘Opportunities in Milling <strong>and</strong> Baking’, by P. Fellows <strong>and</strong> B. Axtell, CTA, 2003<br />
(Annex A). A summary of maintenance requirements is given in Table 5.3<br />
Table 5.3 Details of routine mill maintenance<br />
Daily<br />
Maintenance<br />
Weekly<br />
maintenance<br />
Monthly<br />
maintenance<br />
Mechanical<br />
check <strong>and</strong> grease bearings, replace if faulty<br />
check pulley wheels for cracks or chips <strong>and</strong> replace if necessary to<br />
avoid damaging belts.<br />
check bolts & nuts for tightness.<br />
check the oil level in diesel engines <strong>and</strong> top up with the correct oil if<br />
required.<br />
Electrical<br />
clean flour dust off motors <strong>and</strong> other electrical equipment<br />
when a machine is not in use, make sure that power is switched off at<br />
the mains <strong>and</strong> that equipment has not been left switched on. This is very<br />
important when power cuts occur, because when power returns a<br />
machine that has been left on can injure an operator or cause a fire.<br />
Housekeeping<br />
store tools <strong>and</strong> equipment in pre-determined places to help find them<br />
next time <strong>and</strong> to help notice when they have gone missing.<br />
always keep walkways clear of tools <strong>and</strong> equipment<br />
clean diesel engine cooling fins every day to prevent dust settling <strong>and</strong><br />
causing the engine to overheat <strong>and</strong> eventually seize<br />
when re-fuelling diesel engines, pour the fuel through a filter to prevent<br />
rust deposits in the fuel drum getting mixed with the fuel <strong>and</strong> damaging<br />
the engine<br />
clean the machinery <strong>and</strong> floor<br />
check hammers for wear <strong>and</strong> replace if necessary<br />
check the shaft (especially if locally manufactured machines are not<br />
tested for strength or alignment)<br />
check that locking nuts on the shaft are tight.<br />
check that fan bolts <strong>and</strong> nuts have not loosened as the fan then<br />
becomes very dangerous.<br />
check the bearing mountings as this area is prone to cracking<br />
check the engine oil <strong>and</strong> oil filter on diesel engines <strong>and</strong> change them<br />
every 160 working hours. Change the fuel filter every 320 working<br />
hours.<br />
check the body casting <strong>and</strong> welds for cracks<br />
tighten floor nuts <strong>and</strong> look for any cracks in the mill foundation<br />
check the fan key <strong>and</strong> make sure that the fan is a slide fit on the shaft<br />
for easy removal. If the blades are worn always replace with the correct<br />
thickness of steel <strong>and</strong> then check for balance<br />
check that cables are secured <strong>and</strong> there is no obvious sign of insulation<br />
breakdown<br />
check the acid level in batteries that are used to start diesel engines.<br />
Keep the terminals clean.<br />
If a hammer mill fails to grind efficiently the hammers may be badly worn, <strong>and</strong> they should be<br />
first turned around to use the second edge (Fig. 5.14). When this has worn the hammers<br />
60