PDF Version - Tutorials Point
PDF Version - Tutorials Point
PDF Version - Tutorials Point
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
C++ GOTO STATEMENT<br />
http://www.tuto rialspo int.co m/cplusplus/cpp_g o to _statement.htm<br />
Copyrig ht © tutorialspoint.com<br />
A g oto statement provides an unconditional jump from the g oto to a labeled statement in the same function.<br />
NOTE: Use of g oto statement is hig hly discourag ed because it makes difficult to trace the control flow of a<br />
prog ram, making the prog ram hard to understand and hard to modify. Any prog ram that uses a g oto can be<br />
rewritten so that it doesn't need the g oto.<br />
Syntax:<br />
The syntax of a g oto statement in C++ is:<br />
goto label;<br />
..<br />
.<br />
label: statement;<br />
Where label is an identifier that identifies a labeled statement. A labeled statement is any statement that is<br />
preceded by an identifier followed by a colon (:).<br />
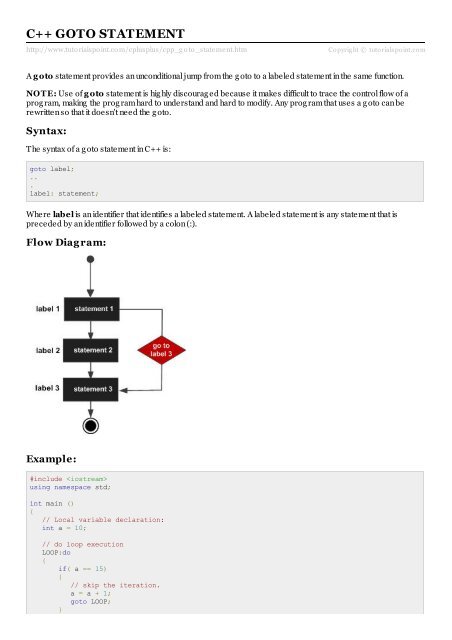
Flow Diag ram:<br />
Example:<br />
#include <br />
using namespace std;<br />
int main ()<br />
{<br />
// Local variable declaration:<br />
int a = 10;<br />
// do loop execution<br />
LOOP:do<br />
{<br />
if( a == 15)<br />
{<br />
// skip the iteration.<br />
a = a + 1;<br />
goto LOOP;<br />
}
cout