Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5.5 Simulation Results<br />
150<br />
OPT−SOL<br />
(a)<br />
Lifetime (S)<br />
100<br />
50<br />
end−to−end rate (bits/s/Hz)<br />
0<br />
0 50 100 150 200 250 300<br />
iteration no.<br />
(b)<br />
300<br />
200<br />
100<br />
HOP1<br />
HOP5<br />
R−Req<br />
0<br />
0 50 100 150 200 250 300<br />
iteration no.<br />
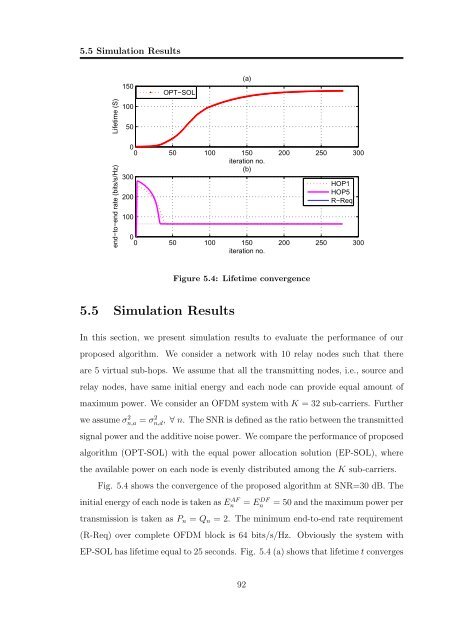
Figure 5.4: Lifetime convergence<br />
5.5 Simulation Results<br />
In this section, we present simulation results to evaluate the performance of our<br />
proposed algorithm. We consider a network with 10 relay nodes such that there<br />
are 5 virtual sub-hops. We assume that all the transmitt<strong>in</strong>g nodes, i.e., source and<br />
relay nodes, have same <strong>in</strong>itial energy and each node can provide equal amount of<br />
maximum power. We consider an <strong>OFDM</strong> system with K = 32 sub-carriers. Further<br />
we assume σn,a 2 = σn,d 2 , ∀ n. The SNR is def<strong>in</strong>ed as the ratio between the transmitted<br />
signal power and the additive noise power. We compare the performance of proposed<br />
algorithm (OPT-SOL) with the equal power allocation solution (EP-SOL), where<br />
the available power on each node is evenly distributed among the K sub-carriers.<br />
Fig. 5.4 shows the convergence of the proposed algorithm at SNR=30 dB. The<br />
<strong>in</strong>itial energy of each node is taken as E AF<br />
n<br />
= E DF<br />
n<br />
= 50 and the maximum power per<br />
transmission is taken as P n = Q n = 2. The m<strong>in</strong>imum end-to-end rate requirement<br />
(R-Req) over complete <strong>OFDM</strong> block is 64 bits/s/Hz. Obviously the system with<br />
EP-SOL has lifetime equal to 25 seconds. Fig. 5.4 (a) shows that lifetime t converges<br />
92