Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
5.6 Summary<br />
Lifetime (S)<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
OPT−SOL<br />
EP−SOL<br />
end−to−end rate (bits/s/Hz)<br />
0<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25 30<br />
SNR (dB)<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
OPT−SOL<br />
EP−SOL<br />
R−Req<br />
0<br />
0 5 10 15 20 25 30<br />
SNR (dB)<br />
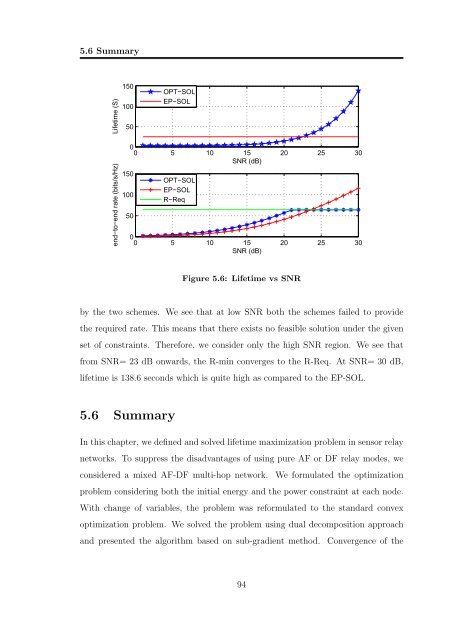
Figure 5.6: Lifetime vs SNR<br />
by the two schemes. We see that at low SNR both the schemes failed to provide<br />
the required rate. This means that there exists no feasible solution under the given<br />
set of constra<strong>in</strong>ts. Therefore, we consider only the high SNR region. We see that<br />
from SNR= 23 dB onwards, the R-m<strong>in</strong> converges to the R-Req. At SNR= 30 dB,<br />
lifetime is 138.6 seconds which is quite high as compared to the EP-SOL.<br />
5.6 Summary<br />
In this chapter, we def<strong>in</strong>ed and solved lifetime maximization problem <strong>in</strong> sensor relay<br />
networks. To suppress the disadvantages of us<strong>in</strong>g pure AF or DF relay modes, we<br />
considered a mixed AF-DF multi-hop network. We formulated the optimization<br />
problem consider<strong>in</strong>g both the <strong>in</strong>itial energy and the power constra<strong>in</strong>t at each node.<br />
With change of variables, the problem was reformulated to the standard convex<br />
optimization problem. We solved the problem us<strong>in</strong>g dual decomposition approach<br />
and presented the algorithm based on sub-gradient method. Convergence of the<br />
94