Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Resource Allocation in OFDM Based Wireless Relay Networks ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
5.5 Simulation Results<br />
350<br />
300<br />
250<br />
E=50<br />
E=60<br />
E=70<br />
E=80<br />
E=90<br />
Lifetime (S)<br />
200<br />
150<br />
100<br />
50<br />
55 60 65 70 75<br />
R−Req<br />
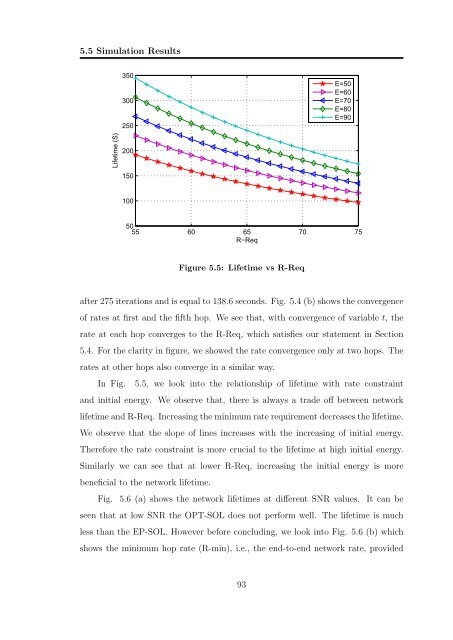
Figure 5.5: Lifetime vs R-Req<br />
after 275 iterations and is equal to 138.6 seconds. Fig. 5.4 (b) shows the convergence<br />
of rates at first and the fifth hop. We see that, with convergence of variable t, the<br />
rate at each hop converges to the R-Req, which satisfies our statement <strong>in</strong> Section<br />
5.4. For the clarity <strong>in</strong> figure, we showed the rate convergence only at two hops. The<br />
rates at other hops also converge <strong>in</strong> a similar way.<br />
In Fig. 5.5, we look <strong>in</strong>to the relationship of lifetime with rate constra<strong>in</strong>t<br />
and <strong>in</strong>itial energy. We observe that, there is always a trade off between network<br />
lifetime and R-Req. Increas<strong>in</strong>g the m<strong>in</strong>imum rate requirement decreases the lifetime.<br />
We observe that the slope of l<strong>in</strong>es <strong>in</strong>creases with the <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g of <strong>in</strong>itial energy.<br />
Therefore the rate constra<strong>in</strong>t is more crucial to the lifetime at high <strong>in</strong>itial energy.<br />
Similarly we can see that at lower R-Req, <strong>in</strong>creas<strong>in</strong>g the <strong>in</strong>itial energy is more<br />
beneficial to the network lifetime.<br />
Fig. 5.6 (a) shows the network lifetimes at different SNR values. It can be<br />
seen that at low SNR the OPT-SOL does not perform well. The lifetime is much<br />
less than the EP-SOL. However before conclud<strong>in</strong>g, we look <strong>in</strong>to Fig. 5.6 (b) which<br />
shows the m<strong>in</strong>imum hop rate (R-m<strong>in</strong>), i.e., the end-to-end network rate, provided<br />
93