AJ Katalog Radik 012006 finish.indd - Seltron
AJ Katalog Radik 012006 finish.indd - Seltron
AJ Katalog Radik 012006 finish.indd - Seltron
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
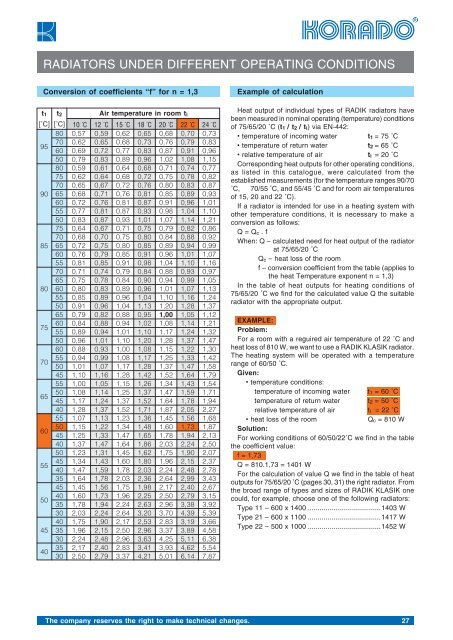
RADIATORS UNDER DIFFERENT OPERATING CONDITIONS<br />
Conversion of coefficients “f” for n = 1,3<br />
Example of calculation<br />
t 1 t 2<br />
[°C] [°C]<br />
80<br />
70<br />
95<br />
60<br />
50<br />
80<br />
75<br />
70<br />
90 65<br />
60<br />
55<br />
50<br />
75<br />
70<br />
85 65<br />
60<br />
55<br />
70<br />
65<br />
80 60<br />
55<br />
50<br />
65<br />
60<br />
75<br />
55<br />
50<br />
60<br />
55<br />
70<br />
50<br />
45<br />
55<br />
50<br />
65<br />
45<br />
40<br />
55<br />
50<br />
60<br />
45<br />
40<br />
50<br />
45<br />
55<br />
40<br />
35<br />
45<br />
40<br />
50<br />
35<br />
30<br />
40<br />
45 35<br />
30<br />
35<br />
40<br />
30<br />
Air temperature in room t i<br />
10 °C 12 °C 15 °C 18 °C 20 °C 22 °C 24 °C<br />
0,57 0,59 0,62 0,65 0,68 0,70 0,73<br />
0,62 0,65 0,68 0,73 0,76 0,79 0,83<br />
0,69 0,72 0,77 0,83 0,87 0,91 0,96<br />
0,79 0,83 0,89 0,96 1,02 1,08 1,15<br />
0,59 0,61 0,64 0,68 0,71 0,74 0,77<br />
0,62 0,64 0,68 0,72 0,75 0,78 0,82<br />
0,65 0,67 0,72 0,76 0,80 0,83 0,87<br />
0,68 0,71 0,76 0,81 0,85 0,89 0,93<br />
0,72 0,76 0,81 0,87 0,91 0,96 1,01<br />
0,77 0,81 0,87 0,93 0,98 1,04 1,10<br />
0,83 0,87 0,93 1,01 1,07 1,14 1,21<br />
0,64 0,67 0,71 0,75 0,79 0,82 0,86<br />
0,68 0,70 0,75 0,80 0,84 0,88 0,92<br />
0,72 0,75 0,80 0,85 0,89 0,94 0,99<br />
0,76 0,79 0,85 0,91 0,96 1,01 1,07<br />
0,81 0,85 0,91 0,98 1,04 1,10 1,16<br />
0,71 0,74 0,79 0,84 0,88 0,93 0,97<br />
0,75 0,78 0,84 0,90 0,94 0,99 1,05<br />
0,80 0,83 0,89 0,96 1,01 1,07 1,13<br />
0,85 0,89 0,96 1,04 1,10 1,16 1,24<br />
0,91 0,96 1,04 1,13 1,20 1,28 1,37<br />
0,79 0,82 0,88 0,95 1,00 1,05 1,12<br />
0,84 0,88 0,94 1,02 1,08 1,14 1,21<br />
0,89 0,94 1,01 1,10 1,17 1,24 1,32<br />
0,96 1,01 1,10 1,20 1,28 1,37 1,47<br />
0,88 0,93 1,00 1,08 1,15 1,22 1,30<br />
0,94 0,99 1,08 1,17 1,25 1,33 1,42<br />
1,01 1,07 1,17 1,28 1,37 1,47 1,58<br />
1,10 1,16 1,28 1,42 1,52 1,64 1,79<br />
1,00 1,05 1,15 1,26 1,34 1,43 1,54<br />
1,08 1,14 1,25 1,37 1,47 1,59 1,71<br />
1,17 1,24 1,37 1,52 1,64 1,78 1,94<br />
1,28 1,37 1,52 1,71 1,87 2,05 2,27<br />
1,07 1,13 1,23 1,36 1,45 1,56 1,68<br />
1,15 1,22 1,34 1,48 1,60 1,73 1,87<br />
1,25 1,33 1,47 1,65 1,78 1,94 2,13<br />
1,37 1,47 1,64 1,86 2,03 2,24 2,50<br />
1,23 1,31 1,45 1,62 1,75 1,90 2,07<br />
1,34 1,43 1,60 1,80 1,96 2,15 2,37<br />
1,47 1,59 1,78 2,03 2,24 2,48 2,78<br />
1,64 1,78 2,03 2,36 2,64 2,99 3,43<br />
1,45 1,56 1,75 1,98 2,17 2,40 2,67<br />
1,60 1,73 1,96 2,25 2,50 2,79 3,15<br />
1,78 1,94 2,24 2,63 2,96 3,38 3,92<br />
2,03 2,24 2,64 3,20 3,70 4,39 5,39<br />
1,75 1,90 2,17 2,53 2,83 3,19 3,66<br />
1,96 2,15 2,50 2,96 3,37 3,89 4,58<br />
2,24 2,48 2,96 3,63 4,25 5,11 6,38<br />
2,17 2,40 2,83 3,41 3,93 4,62 5,54<br />
2,50 2,79 3,37 4,21 5,01 6,14 7,87<br />
Heat output of individual types of RADIK radiators have<br />
been measured in nominal operating (temperature) conditions<br />
of 75/65/20 °C (t 1 / t 2 / t i) via EN-442:<br />
• temperature of incoming water t 1 = 75 °C<br />
• temperature of return water t 2 = 65 °C<br />
• relative temperature of air t i = 20 °C<br />
Corresponding heat outputs for other operating conditions,<br />
as listed in this catalogue, were calculated from the<br />
established measurements (for the temperature ranges 90/70<br />
°C, 70/55 °C, and 55/45 °C and for room air temperatures<br />
of 15, 20 and 22 °C).<br />
If a radiator is intended for use in a heating system with<br />
other temperature conditions, it is necessary to make a<br />
conversion as follows:<br />
Q = Q c . f<br />
When: Q – calculated need for heat output of the radiator<br />
at 75/65/20 °C<br />
Q c – heat loss of the room<br />
f – conversion coefficient from the table (applies to<br />
the heat Temperature exponent n = 1,3)<br />
In the table of heat outputs for heating conditions of<br />
75/65/20 °C we find for the calculated value Q the suitable<br />
radiator with the appropriate output.<br />
EXAMPLE:<br />
Problem:<br />
For a room with a reguired air temperature of 22 °C and<br />
heat loss of 810 W, we want to use a RADIK KLASIK radiator.<br />
The heating system will be operated with a temperature<br />
range of 60/50 °C.<br />
Given:<br />
• temperature conditions:<br />
temperature of incoming water t 1 = 60 °C<br />
temperature of return water t 2 = 50 °C<br />
relative temperature of air t i = 22 °C<br />
• heat loss of the room<br />
Q c = 810 W<br />
Solution:<br />
For working conditions of 60/50/22°C we find in the table<br />
the coefficient value:<br />
f = 1,73<br />
Q = 810.1,73 = 1401 W<br />
For the calculation of value Q we find in the table of heat<br />
outputs for 75/65/20 °C (pages 30, 31) the right radiator. From<br />
the broad range of types and sizes of RADIK KLASIK one<br />
could, for example, choose one of the following radiators:<br />
Type 11 – 600 x 1400 .....................................1403 W<br />
Type 21 – 600 x 1100 .....................................1417 W<br />
Type 22 – 500 x 1000 .....................................1452 W<br />
The company reserves the right to make technical changes. 27