Gasoline and Diesel Fuel Injection: Operation ... - Pearson Canada
Gasoline and Diesel Fuel Injection: Operation ... - Pearson Canada
Gasoline and Diesel Fuel Injection: Operation ... - Pearson Canada
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
704 CHAPTER 29<br />
Testing a <strong>Gasoline</strong> <strong>Fuel</strong> Injector Using a Digital Storage Oscillocope—continued<br />
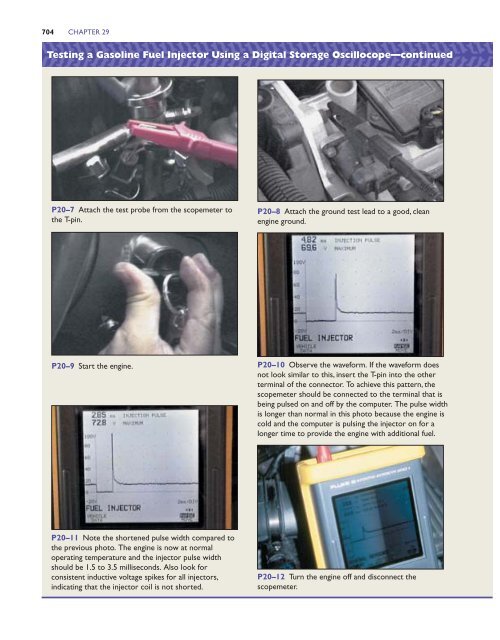
P20–7 Attach the test probe from the scopemeter to<br />
the T-pin.<br />
P20–8 Attach the ground test lead to a good, clean<br />
engine ground.<br />
P20–9 Start the engine. P20–10 Observe the waveform. If the waveform does<br />
not look similar to this, insert the T-pin into the other<br />
terminal of the connector. To achieve this pattern, the<br />
scopemeter should be connected to the terminal that is<br />
being pulsed on <strong>and</strong> off by the computer. The pulse width<br />
is longer than normal in this photo because the engine is<br />
cold <strong>and</strong> the computer is pulsing the injector on for a<br />
longer time to provide the engine with additional fuel.<br />
P20–11 Note the shortened pulse width compared to<br />
the previous photo. The engine is now at normal<br />
operating temperature <strong>and</strong> the injector pulse width<br />
should be 1.5 to 3.5 milliseconds. Also look for<br />
consistent inductive voltage spikes for all injectors,<br />
indicating that the injector coil is not shorted.<br />
P20–12 Turn the engine off <strong>and</strong> disconnect the<br />
scopemeter.