Lecture 9: Linear Programming
Lecture 9: Linear Programming
Lecture 9: Linear Programming
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
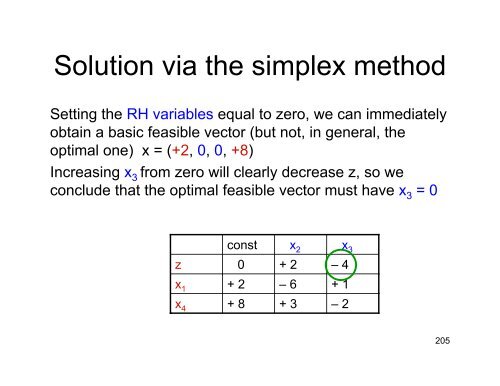
Solution via the simplex method<br />
Setting the RH variables equal to zero, we can immediately<br />
obtain a basic feasible vector (but not, in general, the<br />
optimal one) x = (+2, 0, 0, +8)<br />
Increasing x 3 from zero will clearly decrease z, so we<br />
conclude that the optimal feasible vector must have x 3 = 0<br />
const<br />
x 2 x 3<br />
z 0 + 2 –4<br />
x 1 + 2 –6 + 1<br />
x 4 + 8 + 3 –2<br />
205