Principles of MRI - Department of Radiology
Principles of MRI - Department of Radiology
Principles of MRI - Department of Radiology
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
1995<br />
1996<br />
1997<br />
1998<br />
1999<br />
2000<br />
2001<br />
2002<br />
2003<br />
2004<br />
2005<br />
2006<br />
2007<br />
2008<br />
2009<br />
2010<br />
2011<br />
2012<br />
Evolution <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong>:<br />
Focus on MSK <strong>MRI</strong><br />
The Evolution <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong><br />
Radiographs<br />
Tomography<br />
CT<br />
MR<br />
Signal<br />
Sequences<br />
Coils<br />
Magnets<br />
Safety<br />
Hardware<br />
PA<br />
www.schreibman.info<br />
© 2011 Ken L Schreibman, PhD/MD<br />
Jump to last<br />
slide viewed<br />
Focus on Musculoskeletal <strong>MRI</strong><br />
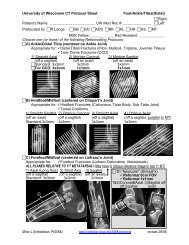
For Joints: Need 3 Views!<br />
PIP<br />
Obl<br />
PIP<br />
Lat<br />
Jump to<br />
next slide<br />
PIP<br />
Slide 7 <strong>of</strong> 88<br />
The Evolution <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong><br />
Radiographs<br />
Tomography<br />
CT<br />
MR<br />
Signal<br />
Sequences<br />
Coils<br />
Magnets<br />
Safety<br />
Hardware<br />
www.schreibman.info British Journal <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong><br />
© 2011 Ken L Schreibman, PhD/MD<br />
8:733-751,1935<br />
page 2 <strong>of</strong> 15<br />
Jump to last<br />
slide viewed<br />
Focus on Musculoskeletal <strong>MRI</strong><br />
Tomography: Small Step Forward<br />
To overcome<br />
flat 2D nature <strong>of</strong><br />
radiographs…<br />
‣ Structures in the<br />
Focal Plane <br />
are in focus.<br />
‣ Structures out <strong>of</strong><br />
focal plane are<br />
blurred out.<br />
‣ At best, we got<br />
blurry pictures.<br />
‣ Long exposures<br />
= high radiation.<br />
1935<br />
Grossmann<br />
Tomograph<br />
Can’t use<br />
this to see<br />
the brain <br />
Focal Plane<br />
Film<br />
Jump to<br />
next slide<br />
Slide 8 <strong>of</strong> 88<br />
The Evolution <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong><br />
Radiographs<br />
Tomography<br />
CT<br />
MR<br />
Signal<br />
Sequences<br />
Coils<br />
Magnets<br />
Safety<br />
Hardware<br />
Focus on Musculoskeletal <strong>MRI</strong><br />
CT: Giant Leap Forward<br />
CT: Computed Tomography (Tomo [Gr]: part, slice)<br />
CAT: Computed Axial Tomography<br />
1917 Johann Radon, Austrian mathematician, proved<br />
image <strong>of</strong> a 3D object could be reconstructed from an<br />
infinite number <strong>of</strong> 2D projection images <strong>of</strong> the object.<br />
‣ Had to await the advent <strong>of</strong> mainframe<br />
computers in the 1970’s.<br />
The Evolution <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong><br />
Focus on Musculoskeletal <strong>MRI</strong><br />
Hounsfield & EMI Brain Scanner<br />
Radiographs 1972: Godfrey Hounsfield, a British electrical engineer<br />
Tomography at EMI Laboratories, developed EMI Brain Scanner.<br />
CT<br />
‣Finally, could see through the skull into the brain!<br />
Awarded Nobel Prize for Medicine 1979; Knighted 1981.<br />
MR<br />
“Hounsfield Units” is the scale we use to measure CT density.<br />
Signal ‣ EMI: “Electric and Musical Industries”<br />
Sequences<br />
Coils<br />
Magnets<br />
Safety<br />
Hardware<br />
www.schreibman.info<br />
© 2011 Ken L Schreibman, PhD/MD<br />
www.wikipedia.com<br />
Jump to last<br />
slide viewed<br />
Jump to<br />
next slide<br />
Slide 9 <strong>of</strong> 88<br />
www.schreibman.info www.sciencemuseum.org.uk<br />
© 2011 Ken L Schreibman, PhD/MD<br />
Jump to last<br />
slide viewed<br />
Jump to<br />
next slide<br />
Slide 10 <strong>of</strong> 88<br />
The Evolution <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong><br />
Radiographs<br />
Tomography<br />
CT<br />
MR<br />
Signal<br />
Sequences<br />
Coils<br />
Magnets<br />
Safety<br />
Hardware<br />
www.schreibman.info<br />
© 2011 Ken L Schreibman, PhD/MD<br />
Jump to last<br />
slide viewed<br />
Focus on Musculoskeletal <strong>MRI</strong><br />
Why CT is So Great<br />
Can see the brain<br />
‣Strokes, bleeds, tumors<br />
Can see organs (lungs, liver, bowel)<br />
‣Tumors, trauma, acute/chronic diseases<br />
Can see fractures otherwise missed<br />
‣Cervical spine, pelvis<br />
And now with ultra-fast, multi-slice…<br />
‣Can scan the heart in a single beat!<br />
Can see coronary arteries, pulmonary emboli<br />
Hospitals have CT scanners in the ER<br />
Jump to<br />
next slide<br />
Slide 11 <strong>of</strong> 88<br />
The Evolution <strong>of</strong> <strong>Radiology</strong><br />
Radiographs<br />
Tomography<br />
CT<br />
MR<br />
Signal<br />
Sequences<br />
Coils<br />
Magnets<br />
Safety<br />
Hardware<br />
25%<br />
20%<br />
15%<br />
10%<br />
5%<br />
0%<br />
www.schreibman.info<br />
© 2011 Ken L Schreibman, PhD/MD<br />
Jump to last<br />
slide viewed<br />
Focus on Musculoskeletal <strong>MRI</strong><br />
CT Usage Increasing in ERs<br />
Percentage <strong>of</strong> patients seen in US ERs who get CT<br />
30%<br />
26%<br />
National Trends in CT Use in the<br />
22%<br />
Emergency <strong>Department</strong>: 1995-2007<br />
20%<br />
presented at RSNA 11/29/2010 17%<br />
15%<br />
David B. Larson, MD, MBA et. al.<br />
Extrapolated<br />
3% 3% 3% 4% 5% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% 10% 11% 13% Data<br />
Sample Data<br />
radiology.rsna.org<br />
Jump to<br />
next slide<br />
Slide 12 <strong>of</strong> 88<br />
©Ken L Schreibman, PhD/MD 10/10/11 www.schreibman.info