Lecture Notes in Advanced Thermodynamics
Lecture Notes in Advanced Thermodynamics
Lecture Notes in Advanced Thermodynamics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
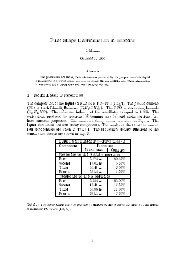
quantity variables Gibbs relation<br />
energy E(S, V, M) dE = T dS − pdV + µdM<br />
Helmholtz free energy F (T, V, M) dF = −SdT − pdV + µdM<br />
enthalpy H(S, p, M) dH = T dS + V dp + µdM<br />
Gibbs free energy G(T, p, M) dG = −SdT + V dp + µdM<br />
Table 2: Important thermodynamic potentials - variables<br />
2.3 Densities, specific quantities<br />
– the extensive and <strong>in</strong>tensive properties are constra<strong>in</strong>ts<br />
– one of the extensive variables can be elim<strong>in</strong>ated<br />
– it can be useful to choose a reference variable<br />
– usually the volume (densities) and the mass (specific quantities) are<br />
used for reference<br />
2.3.1 Densities<br />
transformation of the basic state variables<br />
– energy density:<br />
ε := E V<br />
– mass density:<br />
ρ := M V<br />
transformation of the state functions<br />
– the (E, V, M) state space can be simplified to (ε, ρ)<br />
– consider<strong>in</strong>g an extensive state function:<br />
( E<br />
ˆf(ε, ρ) := f (ε, 1, ρ) = f<br />
V , 1, M )<br />
= V f ( E<br />
, 1, )<br />
M<br />
V V<br />
=<br />
V V<br />
f(E, V, M)<br />
V<br />
specially:<br />
Ê = ε;<br />
ˆM = ρ<br />
12