TO 35-1-3 - Robins Air Force Base
TO 35-1-3 - Robins Air Force Base
TO 35-1-3 - Robins Air Force Base
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>TO</strong> <strong>35</strong>-1-3<br />
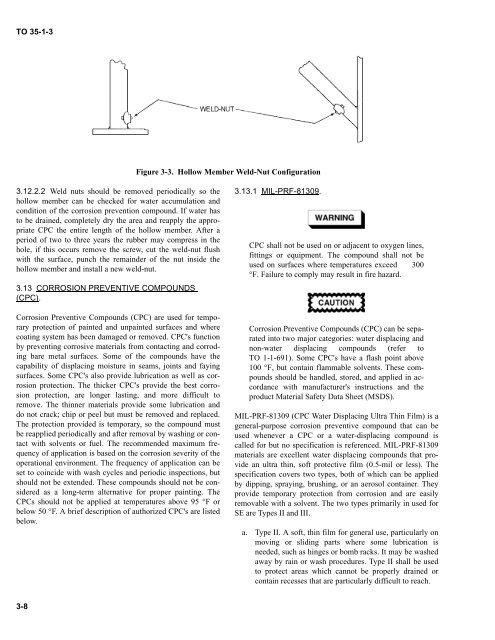
Figure 3-3. Hollow Member Weld-Nut Configuration<br />
3.12.2.2 Weld nuts should be removed periodically so the<br />
hollow member can be checked for water accumulation and<br />
condition of the corrosion prevention compound. If water has<br />
to be drained, completely dry the area and reapply the appropriate<br />
CPC the entire length of the hollow member. After a<br />
period of two to three years the rubber may compress in the<br />
hole, if this occurs remove the screw, cut the weld-nut flush<br />
with the surface, punch the remainder of the nut inside the<br />
hollow member and install a new weld-nut.<br />
3.13 CORROSION PREVENTIVE COMPOUNDS<br />
(CPC).<br />
Corrosion Preventive Compounds (CPC) are used for temporary<br />
protection of painted and unpainted surfaces and where<br />
coating system has been damaged or removed. CPC's function<br />
by preventing corrosive materials from contacting and corroding<br />
bare metal surfaces. Some of the compounds have the<br />
capability of displacing moisture in seams, joints and faying<br />
surfaces. Some CPC's also provide lubrication as well as corrosion<br />
protection. The thicker CPC's provide the best corrosion<br />
protection, are longer lasting, and more difficult to<br />
remove. The thinner materials provide some lubrication and<br />
do not crack; chip or peel but must be removed and replaced.<br />
The protection provided is temporary, so the compound must<br />
be reapplied periodically and after removal by washing or contact<br />
with solvents or fuel. The recommended maximum frequency<br />
of application is based on the corrosion severity of the<br />
operational environment. The frequency of application can be<br />
set to coincide with wash cycles and periodic inspections, but<br />
should not be extended. These compounds should not be considered<br />
as a long-term alternative for proper painting. The<br />
CPCs should not be applied at temperatures above 95 °F or<br />
below 50 °F. A brief description of authorized CPC's are listed<br />
below.<br />
3.13.1 MIL-PRF-81309.<br />
CPC shall not be used on or adjacent to oxygen lines,<br />
fittings or equipment. The compound shall not be<br />
used on surfaces where temperatures exceed 300<br />
°F. Failure to comply may result in fire hazard.<br />
Corrosion Preventive Compounds (CPC) can be separated<br />
into two major categories: water displacing and<br />
non-water displacing compounds (refer to<br />
<strong>TO</strong> 1-1-691). Some CPC's have a flash point above<br />
100 °F, but contain flammable solvents. These compounds<br />
should be handled, stored, and applied in accordance<br />
with manufacturer's instructions and the<br />
product Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS).<br />
MIL-PRF-81309 (CPC Water Displacing Ultra Thin Film) is a<br />
general-purpose corrosion preventive compound that can be<br />
used whenever a CPC or a water-displacing compound is<br />
called for but no specification is referenced. MIL-PRF-81309<br />
materials are excellent water displacing compounds that provide<br />
an ultra thin, soft protective film (0.5-mil or less). The<br />
specification covers two types, both of which can be applied<br />
by dipping, spraying, brushing, or an aerosol container. They<br />
provide temporary protection from corrosion and are easily<br />
removable with a solvent. The two types primarily in used for<br />
SE are Types II and III.<br />
a. Type II. A soft, thin film for general use, particularly on<br />
moving or sliding parts where some lubrication is<br />
needed, such as hinges or bomb racks. It may be washed<br />
away by rain or wash procedures. Type II shall be used<br />
to protect areas which cannot be properly drained or<br />
contain recesses that are particularly difficult to reach.<br />
3-8