Life Cycle Assessment of Fiber Composites_final__rättad
Life Cycle Assessment of Fiber Composites_final__rättad
Life Cycle Assessment of Fiber Composites_final__rättad
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
4.3. <strong>Life</strong> <strong>Cycle</strong> for Balsa Core and PVC Foam Sandwich<br />
Super Structure<br />
Material<br />
Energy<br />
Fuel<br />
Weight<br />
transported<br />
Manufacturing Operation Scrapping<br />
Landfill<br />
Waste<br />
Recycling<br />
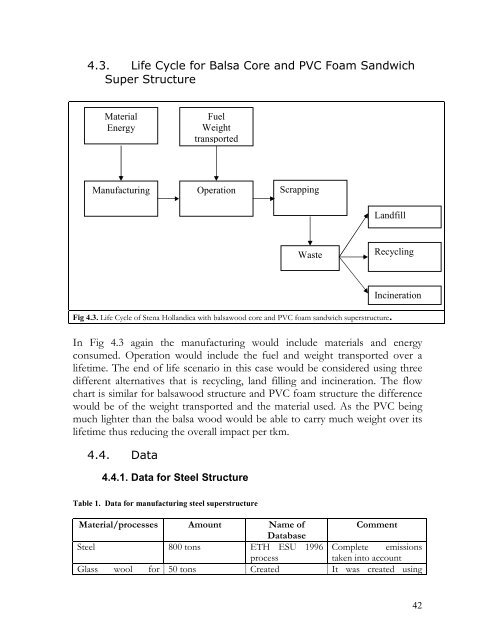
Fig 4.3. <strong>Life</strong> <strong>Cycle</strong> <strong>of</strong> Stena Hollandica with balsawood core and PVC foam sandwich superstructure.<br />
In Fig 4.3 again the manufacturing would include materials and energy<br />
consumed. Operation would include the fuel and weight transported over a<br />
lifetime. The end <strong>of</strong> life scenario in this case would be considered using three<br />
different alternatives that is recycling, land filling and incineration. The flow<br />
chart is similar for balsawood structure and PVC foam structure the difference<br />
would be <strong>of</strong> the weight transported and the material used. As the PVC being<br />
much lighter than the balsa wood would be able to carry much weight over its<br />
lifetime thus reducing the overall impact per tkm.<br />
4.4. Data<br />
4.4.1. Data for Steel Structure<br />
Incineration<br />
Table 1. Data for manufacturing steel superstructure<br />
Material/processes Amount Name <strong>of</strong><br />
Comment<br />
Database<br />
Steel 800 tons ETH ESU 1996 Complete emissions<br />
process<br />
taken into account<br />
Glass wool for 50 tons Created It was created using<br />
42