Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Design Guide - Solvay Plastics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
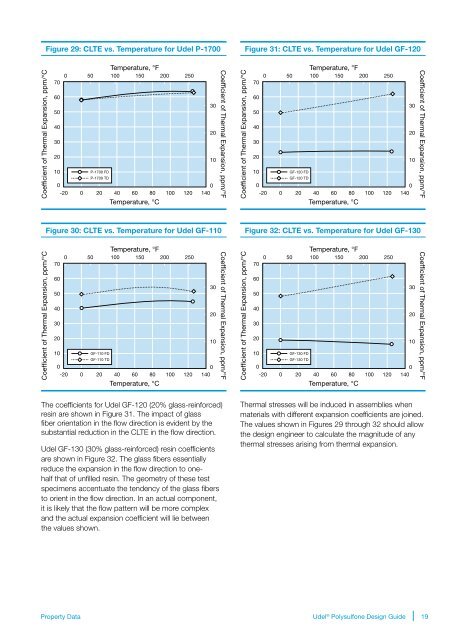
Figure 29: CLTE vs. Temperature for Udel P-1700<br />
Figure 31: CLTE vs. Temperature for Udel GF-120<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°C<br />
Temperature, °F<br />
0 50 100 150 200 250<br />
70<br />
60<br />
30<br />
50<br />
40<br />
20<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
10<br />
P-1700 FD<br />
P-1700 TD<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140<br />
Temperature, °C<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°F<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°C<br />
Temperature, °F<br />
0 50 100 150 200 250<br />
70<br />
60<br />
30<br />
50<br />
40<br />
20<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
10<br />
GF-120 FD<br />
GF-120 TD<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140<br />
Temperature, °C<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°F<br />
Figure 30: CLTE vs. Temperature for Udel GF-110<br />
Figure 32: CLTE vs. Temperature for Udel GF-130<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°C<br />
Temperature, °F<br />
0 50 100 150 200 250<br />
70<br />
60<br />
30<br />
50<br />
40<br />
20<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
10<br />
GF-110 FD<br />
GF-110 TD<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140<br />
Temperature, °C<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°F<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°C<br />
Temperature, °F<br />
0 50 100 150 200 250<br />
70<br />
60<br />
30<br />
50<br />
40<br />
20<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
10<br />
GF-130 FD<br />
GF-130 TD<br />
0<br />
0<br />
-20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140<br />
Temperature, °C<br />
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion, ppm/°F<br />
The coefficients for Udel GF-120 (20% glass-reinforced)<br />
resin are shown in Figure 31. The impact of glass<br />
fiber orientation in the flow direction is evident by the<br />
substantial reduction in the CLTE in the flow direction.<br />
Udel GF-130 (30% glass-reinforced) resin coefficients<br />
are shown in Figure 32. The glass fibers essentially<br />
reduce the expansion in the flow direction to onehalf<br />
that of unfilled resin. The geometry of these test<br />
specimens accentuate the tendency of the glass fibers<br />
to orient in the flow direction. In an actual component,<br />
it is likely that the flow pattern will be more complex<br />
and the actual expansion coefficient will lie between<br />
the values shown.<br />
Thermal stresses will be induced in assemblies when<br />
materials with different expansion coefficients are joined.<br />
The values shown in Figures 29 through 32 should allow<br />
the design engineer to calculate the magnitude of any<br />
thermal stresses arising from thermal expansion.<br />
Property Data<br />
Udel ® Polysulfone <strong>Design</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
19