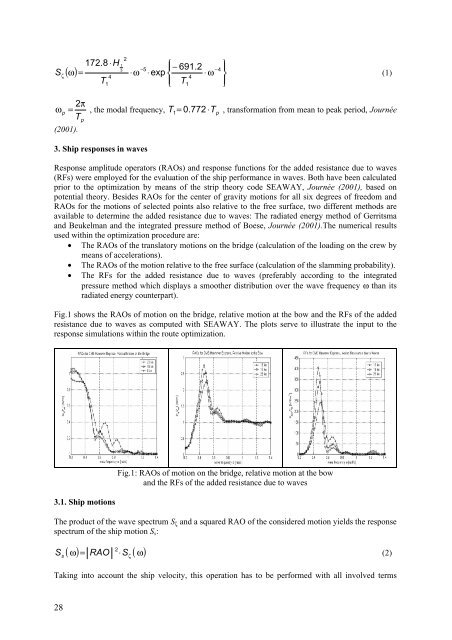
- Page 1 and 2: 3 rd International Conference on Co
- Page 3 and 4: Patrick Hupe, Uwe Langbecker, Mubas
- Page 5 and 6: Towards Intelligent Simulation-Base
- Page 7 and 8: ectly damage in terms of greenhouse
- Page 9 and 10: Fig.7: FEA of a catamaran made of c
- Page 11 and 12: Set the small parts fixing the part
- Page 13 and 14: main benefit of 3-d design lies in
- Page 15 and 16: Applic. Mar. Industries, COMPIT, Ha
- Page 17 and 18: Use of Genetic Algorithms in Propel
- Page 19 and 20: 3. Fitness Function Formulation The
- Page 21 and 22: where µ α and µ θ are the chose
- Page 23 and 24: From another point of view and unde
- Page 25 and 26: Y X Benchmark First Optimum Fig.8:
- Page 27: A Systematic Study on Posing and So
- Page 31 and 32: 4.4. Optimization with modeFRONTIER
- Page 33 and 34: Fig.5: SIMPLEX optimization and Par
- Page 35 and 36: References HOFFSCHILDT, M.; BIDLOT,
- Page 37 and 38: 2.2. Tribon Product Information Mod
- Page 39 and 40: 3. New Process The new process is b
- Page 41 and 42: 4. Conclusions and next step The ne
- Page 43 and 44: 2. E-Commerce of goods versus servi
- Page 45 and 46: Main steps on ePING’s road-map ar
- Page 47 and 48: anon. client new client registered
- Page 49 and 50: Preparing an offer can be hierarchi
- Page 51 and 52: Acknowledgment This work was partia
- Page 53 and 54: The focus within this paper is the
- Page 55 and 56: conditions have to be prevented. Fo
- Page 57 and 58: Ship 2 LPP 182.390 m B 26.00 m T D
- Page 59 and 60: Fig.9: Ship 1; Simulated Crash stop
- Page 61 and 62: Using Simulation in Evaluating Bert
- Page 63 and 64: ship. To shorten the time spent by
- Page 65 and 66: travelled by each SC are totalled t
- Page 67 and 68: around time is the highest against
- Page 69 and 70: to alternative berths instead of pl
- Page 71 and 72: Appendix 1: Data Collected from Con
- Page 73 and 74: Abstract Introduction to BALTPORTS-
- Page 75 and 76: - at the level of operational plann
- Page 77 and 78: - External interoperability - In ad
- Page 79 and 80:
5. Setting up of the Baltic Sub-Reg
- Page 81 and 82:
Robot Applications in the Field of
- Page 83 and 84:
Fig.3: The main components of the D
- Page 85 and 86:
The precision of the process depend
- Page 87 and 88:
The frame is further divided into 2
- Page 89 and 90:
1. Periodicity on the time line, pe
- Page 91 and 92:
Quality measures. Let J be the inst
- Page 93 and 94:
6.2 Mutation A random number out of
- Page 95 and 96:
7.1 Adaptation of Theorem 2 in our
- Page 97 and 98:
8. Conclusions and scope for future
- Page 99 and 100:
meet the needs of the user. Typical
- Page 101 and 102:
2-digit level (e.g., 220 - Engineer
- Page 103 and 104:
eviewed in dialogue boxes and on Ex
- Page 105 and 106:
Fig.3: Example tanker (HMI BRENTON
- Page 107 and 108:
Fig.7: Assigned material tabular en
- Page 109 and 110:
Fig.11: Design ship 2-digit SWBS Re
- Page 111 and 112:
Communication in Ship Design Networ
- Page 113 and 114:
number and volume of communicated i
- Page 115 and 116:
The investigated collaborations are
- Page 117 and 118:
The four principle communication pa
- Page 119 and 120:
6. Information content In design cl
- Page 121 and 122:
References ERIKSTAD, S.O., HAGEN, A
- Page 123 and 124:
intensive. The terminal's own drive
- Page 125 and 126:
A distribution of decision competen
- Page 127 and 128:
the order for planning the task to
- Page 129 and 130:
3.400.000 Total costs 3.200.000 3.0
- Page 131 and 132:
Visualisation of Ship Motions in Wa
- Page 133 and 134:
3.3. Panelisation and information e
- Page 135 and 136:
5.2. 3D visualisation Fig.4: Refere
- Page 137 and 138:
6.2. Examples of the visualisations
- Page 139 and 140:
7. Conclusions The presented toolki
- Page 141 and 142:
Fig.2: Possibilities for robotic in
- Page 143 and 144:
Experiments with the underwater cam
- Page 145 and 146:
Fig.13. and 14: Cleaning of the cha
- Page 147 and 148:
Acknowledgements The authors want t
- Page 149 and 150:
Fig.2: Result of Industrial Enginee
- Page 151 and 152:
2. Industrial engineering system fo
- Page 153 and 154:
4. Next steps In the next phase, th
- Page 155 and 156:
organizations and organizational un
- Page 157 and 158:
artifact’s context and extend the
- Page 159 and 160:
We take the ship survey process, wh
- Page 161 and 162:
device multimedia capabilities: Sur
- Page 163 and 164:
4. Future Work The mobile services
- Page 165 and 166:
FEM Supported Alignment of Power Tr
- Page 167 and 168:
2.2. Causes First researches result
- Page 169 and 170:
Fig.5: Sufficient tooth grip patter
- Page 171 and 172:
4. Alignment of a RoRo vessel’s p
- Page 173 and 174:
4.3. Calibration/Validation of the
- Page 175 and 176:
Optimisation of the Survivability o
- Page 177 and 178:
Table I: Current UK & US Damage Sta
- Page 179 and 180:
Fig.2: Damage Density Distribution,
- Page 181 and 182:
An Air-to-Surface Missile (ASM) is
- Page 183 and 184:
length according to the existing re
- Page 185 and 186:
the use of a stochastic optimizatio
- Page 187 and 188:
Each MOGA loop requires approximate
- Page 189 and 190:
JIASIONOWSKI, A. (2002), An integra
- Page 191 and 192:
Design problems are typically chara
- Page 193 and 194:
o planned: systematic; o ad-hoc: op
- Page 195 and 196:
o Provide justification for decisio
- Page 197 and 198:
o o o o o o Guide the user through
- Page 199 and 200:
- for some systems, the initial com
- Page 201 and 202:
feasible. The practical implementat
- Page 203 and 204:
PARK, J.H.; STORCH, R.L. (2002), "O
- Page 205 and 206:
where: a, b - coefficients (weights
- Page 207 and 208:
C Fig.2: The fuzzy domain of the bu
- Page 209 and 210:
5.2. Ship fuzzy domain in an open a
- Page 211 and 212:
PIETRZYKOWSKI, Z. (2003a), Modellin
- Page 213 and 214:
means that the number of intersecti
- Page 215 and 216:
4. Manipulation of Sets of Data Poi
- Page 217 and 218:
Fig.2: The selection function defin
- Page 219 and 220:
Let us define the root node of a se
- Page 221 and 222:
Fig.4 took up to several minutes on
- Page 223 and 224:
Applying Meta-Models to the Probabi
- Page 225 and 226:
The assessment of the damage stabil
- Page 227 and 228:
Fig.1 shows clearly an important ch
- Page 229 and 230:
one is willing to do, the smaller t
- Page 231 and 232:
Depending on the number of simulati
- Page 233 and 234:
Since none of the points of the lat
- Page 235 and 236:
CHEN, S.; WANG, L.; WU, X.; WANG, X
- Page 237 and 238:
alance between ship resistance and
- Page 239 and 240:
frequent movements of the pitch tha
- Page 241 and 242:
"commanding" by itself since a vari
- Page 243 and 244:
The numbers shown in the 3 rd row o
- Page 245 and 246:
angle of attack of the water flow o
- Page 247 and 248:
stationary, i.e. all variables rema
- Page 249 and 250:
the engine map runs through the ove
- Page 251 and 252:
References GRIMMELIUS, H.T.; STAPER
- Page 253 and 254:
their output to be random too. Runn
- Page 255 and 256:
simulation runs. It typically takes
- Page 257 and 258:
When the system initiates, the star
- Page 259 and 260:
The user is guided through various
- Page 261 and 262:
• Port Planning & Development •
- Page 263 and 264:
Knowledge-based Concurrent Engineer
- Page 265 and 266:
or puts components aside to make mo
- Page 267 and 268:
Technical specs Make preliminary ca
- Page 269 and 270:
ios, and knowledge about the design
- Page 271 and 272:
are applied afterwards, they can be
- Page 273 and 274:
calculations etc.) The product rela
- Page 275 and 276:
For finding the dependency of reque
- Page 277 and 278:
GIASSI, A. (2003), Multidisciplinar
- Page 279 and 280:
already mentioned. It is based on t
- Page 281 and 282:
2.2.2 Geometry Geometry covers the
- Page 283 and 284:
2.3 Simulation The simulation engin
- Page 285 and 286:
As far as the simulation engine inc
- Page 287 and 288:
time results. Table I: Mustering ti
- Page 289 and 290:
simulation means. The required time
- Page 291 and 292:
design consultants. Starting from a
- Page 293 and 294:
different severity, e.g. warning or
- Page 295 and 296:
• Execute calculation (including
- Page 297 and 298:
and ghostscript, Gnuplot, Ghostscri
- Page 299 and 300:
References CASTOR; An open source d
- Page 301 and 302:
an accurate description of a densit
- Page 303 and 304:
(a) UDS and CDS Schemes (b) Gamma S
- Page 305 and 306:
Figure 3: Typical unstructured grid
- Page 307 and 308:
(a) 0 degree (b) 5 degrees - Port s
- Page 309 and 310:
(a) Computations (b) Experiments Fi
- Page 311 and 312:
(a) X/L = +0.10 (b) X/L = +0.20 (c)
- Page 313 and 314:
4 Conclusion This paper has describ
- Page 315 and 316:
State of the art in climbing and wa
- Page 317 and 318:
2.1 REST 1 and REST 2 climbing robo
- Page 319 and 320:
Figure 5: ROWER 1 system. The full
- Page 321 and 322:
Acknowledgements The REST climbing
- Page 323 and 324:
t²Ùvl uwmhÐu \]9|>CUW>¢Hh9|>@
- Page 325 and 326:
á©ÎetÖJu‚ÓuwØ$t²o"t²Ó(
- Page 327 and 328:
ð qwÓ¸tvuwÑÎzs¤×eÕÐhlxÚNl
- Page 329 and 330:
ÖJu‚ÓuwØ›t²o"t²Ós²^hÔ
- Page 331 and 332:
X X X X X X X X Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Z Y Y
- Page 333 and 334:
30 25 20 Conjugate gradient 30 25 2
- Page 335 and 336:
CARENA is a naval architectural sof
- Page 337 and 338:
Fig.6: Cargo vessel carrying “spe
- Page 339 and 340:
used especially for shape optimizat
- Page 341 and 342:
easily given as simple auto-update
- Page 343 and 344:
and mutation concepts for evolving
- Page 345 and 346:
govern agents’ interaction with t
- Page 347 and 348:
Create generation behaviour Sequent
- Page 349 and 350:
Side Casing Hoister Deck Car Deck C
- Page 351 and 352:
The selection of the best individua
- Page 353 and 354:
Appendix A Table A-I: Optimisation
- Page 355 and 356:
2. Project Management tools in ship
- Page 357 and 358:
Fig.1: Example of document properti
- Page 359 and 360:
Fig.4: Example of query view on doc
- Page 361 and 362:
The Product Data Management is comp
- Page 363 and 364:
Abstract Applications of Self-Organ
- Page 365 and 366:
EMERGENT GLOBAL STRUCTURE LOCAL INT
- Page 367 and 368:
dynamically structured, the system
- Page 369 and 370:
After a leakage has been detected,
- Page 371 and 372:
EXIT door door corridor exit device
- Page 373 and 374:
adaptive. Furthermore, from a imple
- Page 375 and 376:
The main objective for our approach
- Page 377 and 378:
LUCAS, C. (2003), Self-organizing s
- Page 379 and 380:
• As a result of the above-mentio
- Page 381 and 382:
Table I: Exemplary matching of Refe
- Page 383 and 384:
Yard Program time Mile-stone Plan d
- Page 385 and 386:
In the following we start with a di
- Page 387 and 388:
Material Information Machines Proje
- Page 389 and 390:
module (SpaceMan) supports the allo
- Page 391 and 392:
ÖجРÆÙÖÐ ÆØÛÓÖ× ÓÖ
- Page 393 and 394:
ÙÖ ½ ÌÝÔÐ ÙÐÐÓÖÑ Ø×
- Page 395 and 396:
³× ÖØÖÓÒ Ñ×ÙÖ Ó Ø Ö
- Page 397 and 398:
ÑÓÖ ÙÖØÐݸ Ö Ó ÓÚÖ
- Page 399 and 400:
10 10 Exp ANN Exp ANN 7.5 7.5 Cr [x
- Page 401 and 402:
7 Cr [x 1000] 6 5 4 3 2 0.2 0.4 0.6
- Page 403 and 404:
Automation Tools in the Design Proc
- Page 405 and 406:
Fig.1: Visual LISP integrated devel
- Page 407 and 408:
• Bentley’s adoption of VBA •
- Page 409 and 410:
To these outstanding features, it h
- Page 411 and 412:
4.2.1. Automation The objective of
- Page 413 and 414:
• Direction of the start of the c
- Page 415 and 416:
• The FDE program processes the p
- Page 417 and 418:
Database access The FORAN System us
- Page 419 and 420:
A Heuristic for the Container Pre-M
- Page 421 and 422:
When they arrive in the terminal ya
- Page 423 and 424:
(3) The number of all badly placed
- Page 425 and 426:
still greater than zero, the minimu
- Page 427 and 428:
• For each dirty stack s exactly
- Page 429 and 430:
in the remaining 7 instances no mor
- Page 431 and 432:
DOF motion. Then, alter the input f
- Page 433 and 434:
learn of any delay that can occur b
- Page 435 and 436:
40 20 30 10 x-x0 (m) 20 roll (deg)
- Page 437 and 438:
Since, among the velocity component
- Page 439 and 440:
Y (m) -1700 -1500 -1300 -1100 -900
- Page 441 and 442:
system framework, the details of it
- Page 443 and 444:
Real-time Nonlinear Simulation (RNS
- Page 445 and 446:
design modifications are made, and
- Page 447 and 448:
Evacuation Notation - a New Concept
- Page 449 and 450:
• r(t): response time, which acco
- Page 451 and 452:
• The time tk: the time correspon
- Page 453 and 454:
5.1. Quantitative assessment Quanti
- Page 455 and 456:
Table 2: Summary of total and model
- Page 457 and 458:
notation: besides an objective asse
- Page 459 and 460:
Neural Networks Model for Ship Mane
- Page 461 and 462:
&r V G • • r = a = ( uî & & +
- Page 463 and 464:
V a Estimating Forces F Calculating
- Page 465 and 466:
Fig. 5: Error variation for the net
- Page 467 and 468:
Fig 8: Ship's path in Zigzag test 3
- Page 469 and 470:
[4] ALMAN, P.R., BERTSCHE, W.R., BO
- Page 471 and 472:
2 Numerical Methods RANSE methods l
- Page 473 and 474:
As a conclusion of these parameter
- Page 475 and 476:
For correlation of propeller data t
- Page 477 and 478:
quadratic functions result in littl
- Page 479 and 480:
Index by authors Abels 470 Akinfiev