World Congress of Brachytherapy 10-12 May, 2012 - Estro-events.org
World Congress of Brachytherapy 10-12 May, 2012 - Estro-events.org
World Congress of Brachytherapy 10-12 May, 2012 - Estro-events.org
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
S28 <strong>World</strong> <strong>Congress</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Brachytherapy</strong> 20<strong>12</strong><br />
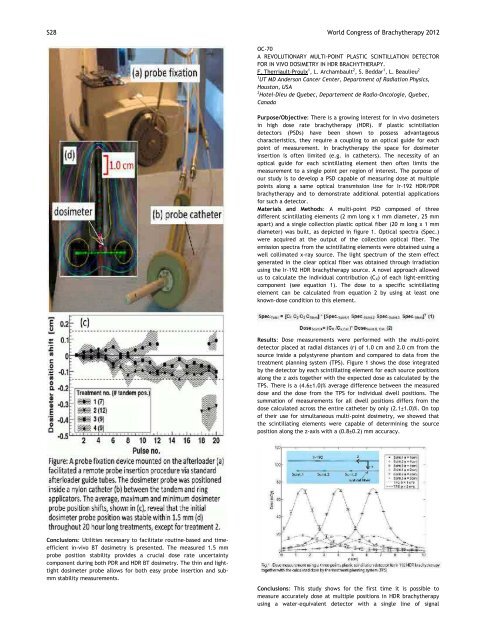
: Utilities necessary to facilitate routinebased and time<br />
efficient invivo BT dosimetry is presented. The measured 1.5 mm<br />
probe position stability provides a crucial dose rate uncertainty<br />
component during both PDR and HDR BT dosimetry. The thin and light<br />
tight dosimeter probe allows for both easy probe insertion and sub<br />
mm stability measurements.<br />
OC70<br />
A REVOLUTIONARY MULTIPOINT PLASTIC SCINTILLATION DETECTOR<br />
FOR IN VIVO DOSIMETRY IN HDR BRACHYTHERAPY.<br />
F. TherriaultProulx 1 , L. Archambault 2 , S. Beddar 1 , L. Beaulieu 2<br />
1<br />
UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, Department <strong>of</strong> Radiation Physics,<br />
Houston, USA<br />
2<br />
HotelDieu de Quebec, Departement de RadioOncologie, Quebec,<br />
Canada<br />
: There is a growing interest for in vivo dosimeters<br />
in high dose rate brachytherapy (HDR). If plastic scintillation<br />
detectors (PSDs) have been shown to possess advantageous<br />
characteristics, they require a coupling to an optical guide for each<br />
point <strong>of</strong> measurement. In brachytherapy the space for dosimeter<br />
insertion is <strong>of</strong>ten limited (e.g. in catheters). The necessity <strong>of</strong> an<br />
optical guide for each scintillating element then <strong>of</strong>ten limits the<br />
measurement to a single point per region <strong>of</strong> interest. The purpose <strong>of</strong><br />
our study is to develop a PSD capable <strong>of</strong> measuring dose at multiple<br />
points along a same optical transmission line for Ir192 HDR/PDR<br />
brachytherapy and to demonstrate additional potential applications<br />
for such a detector.<br />
: A multipoint PSD composed <strong>of</strong> three<br />
different scintillating elements (2 mm long x 1 mm diameter, 25 mm<br />
apart) and a single collection plastic optical fiber (20 m long x 1 mm<br />
diameter) was built, as depicted in figure 1. Optical spectra (Spec.)<br />
were acquired at the output <strong>of</strong> the collection optical fiber. The<br />
emission spectra from the scintillating elements were obtained using a<br />
well collimated xray source. The light spectrum <strong>of</strong> the stem effect<br />
generated in the clear optical fiber was obtained through irradiation<br />
using the Ir192 HDR brachytherapy source. A novel approach allowed<br />
us to calculate the individual contribution (CX) <strong>of</strong> each lightemitting<br />
component (see equation 1). The dose to a specific scintillating<br />
element can be calculated from equation 2 by using at least one<br />
knowndose condition to this element.<br />
: Dose measurements were performed with the multipoint<br />
detector placed at radial distances (r) <strong>of</strong> 1.0 cm and 2.0 cm from the<br />
source inside a polystyrene phantom and compared to data from the<br />
treatment planning system (TPS). Figure 1 shows the dose integrated<br />
by the detector by each scintillating element for each source positions<br />
along the z axis together with the expected dose as calculated by the<br />
TPS. There is a (4.6±1.0)% average difference between the measured<br />
dose and the dose from the TPS for individual dwell positions. The<br />
summation <strong>of</strong> measurements for all dwell positions differs from the<br />
dose calculated across the entire catheter by only (2.1±1.0)%. On top<br />
<strong>of</strong> their use for simultaneous multipoint dosimetry, we showed that<br />
the scintillating elements were capable <strong>of</strong> determining the source<br />
position along the zaxis with a (0.8±0.2) mm accuracy.<br />
: This study shows for the first time it is possible to<br />
measure accurately dose at multiple positions in HDR brachytherapy<br />
using a waterequivalent detector with a single line <strong>of</strong> signal<br />
<strong>World</strong> <strong>Congress</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Brachytherapy</strong> 20<strong>12</strong> S 29<br />
transmission. This will be useful for spatially constrained applications<br />
and will decrease the need for additional catheter implants. Together<br />
with its capacity to determine accurately the source position in space<br />
and all the other advantages known to PSDs, the multipoint PSD has a<br />
bright future and should lead to the development <strong>of</strong> various<br />
applications in HDR/PDR brachytherapy for both in vivo dosimetry and<br />
pretreatment quality assurance.<br />
<br />
OC71<br />
SINGLE NUCLEOTIDE POLYMORPHISMS (SNP'S) ASSOCIATED WITH LATE<br />
RADIATION TOXICITY AFTER PROSTATE BRACHYTHERAPY<br />
N. Leong 1 , M. Parliament 1 , K. Martell 2 , S. Ghosh 3 , N. Pervez 1 , J.<br />
Pedersen 1 , D. Yee 1 , A. Murtha 1 , J. Amanie 1 , N. Usmani 1<br />
1 Cross Cancer Institute, Radiation Oncology, Edmonton, Canada<br />
2 University <strong>of</strong> Alberta, Faculty <strong>of</strong> Medicine, Edmonton, Canada<br />
3 University <strong>of</strong> Alberta, Oncology, Edmonton, Canada<br />
: Excessive toxicity from prostate brachytherapy<br />
treatment may be related to increased radiosensitivity from genetic<br />
polymorphisms. This study was designed to identify particular single<br />
nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP's) that were associated with high<br />
toxicity after therapy in order to determine possible markers for<br />
increased radiation sensitivity<br />
: 349 patients treated with prostate<br />
brachytherapy at the Cross Cancer Institute between 1998 and 20<strong>10</strong><br />
provided saliva samples from which DNA was extracted for this<br />
research ethics board approved study. In the cohort <strong>of</strong> patients with<br />
at least 2 years <strong>of</strong> followup, 41 patients were identified as having<br />
high late toxicity (≥ RTOG grade 2 GI or GU toxicity), and 1<strong>10</strong> patients<br />
were identified as controls without high late toxicity. We analyzed 15<br />
SNP's from 13 genes (MSH6, GSTA1, SOD2, NOS3, GSTP1, ATM, LIG4,<br />
XRCC1, XRCC3, RAD51, TP53, TGFβ1, ERCC2) for correlation with<br />
increased late toxicity. Patient factors and dosimetric parameters<br />
were also collected for the analysis.<br />
: All 15 proposed SNP's demonstrated polymorphism within the<br />
study population. We implemented a univariate analysis, with<br />
Bonferroni correction, to examine the correlation between variant<br />
allele SNP's (versus wild type) and the presence <strong>of</strong> increased toxicity.<br />
This revealed a statistically significant relationship in 3 <strong>of</strong> the SNP's<br />
(p