Profiled Sheeting Design Guide: Part 3 - Barbour Product Search
Profiled Sheeting Design Guide: Part 3 - Barbour Product Search
Profiled Sheeting Design Guide: Part 3 - Barbour Product Search
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
For more information on Marley Eternit visit www.barbourproductsearch.info<br />
Fibre cement rainwater systems<br />
<strong>Design</strong> details<br />
Introduction<br />
Marley Eternit manufacture a comprehensive range<br />
of fibre cement rainwater goods to complement<br />
their range of fibre cement profiled sheeting.<br />
Key<br />
Box = box gutter<br />
HR = half round gutter<br />
BW = boundary wall gutter<br />
VG = valley gutter<br />
This and the following pages provide sufficient<br />
information for the design and specification of<br />
a complete rainwater system.<br />
General guidance<br />
Marley Eternit recommend that designers refer to<br />
BS EN 12056: <strong>Part</strong> 3: 2000 for design<br />
recommendations for drainage of surface water<br />
from roofs.<br />
However, the following method provides a general<br />
guide suitable for 75mm/h rainfall.<br />
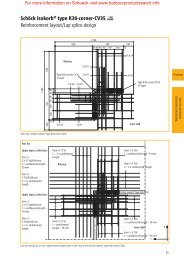
Fig. 1 provides a simple guide to determining the<br />
required sizes of gutter and rainwater pipes from<br />
the length of roof eaves line drained by each outlet<br />
and the length of its upslope (including both slopes<br />
of a roof valley).<br />
To use the nomogram, place a straight edge at the<br />
appropriate points on Scales A and C and read off<br />
the required gutter and rainwater pipe sizes at the<br />
intersection point on Scale B.<br />
Note: Always select gutter and pipe sizes above the<br />
intersection point, never below it.<br />
Scale A Scale B Scale C<br />
20<br />
19<br />
18<br />
17<br />
16<br />
15<br />
14<br />
13<br />
12<br />
11<br />
10<br />
9<br />
8<br />
7<br />
Example<br />
150mm dia.<br />
100mm dia.<br />
75mm dia.<br />
559 x 152 x 406mm BW<br />
305 x 203 mm Box<br />
457 x 152 x 305mm BW<br />
610 x 152 x 229mm VG<br />
406 x 127 x 254mm VG<br />
305 x 152 x 229mm BW<br />
279 x 127 x 178mm BW<br />
457 x 127 x 152mm VG<br />
127 x 152mm Box<br />
200mm HR<br />
150mm HR<br />
25<br />
24<br />
23<br />
22<br />
21<br />
20<br />
19<br />
18<br />
17<br />
16<br />
15<br />
14<br />
13<br />
12<br />
11<br />
10<br />
9<br />
8<br />
Example:<br />
To find the required sizes of valley gutter and<br />
rainwater pipes for two roof slopes each with a<br />
6<br />
125mm HR<br />
7<br />
10m upslope and each 36m long, draining into<br />
6<br />
a common valley.<br />
5<br />
Total upslope length = 2 x 10m = 20m (Scale C).<br />
5<br />
Assume each rainwater pipe drains 12m of gutter<br />
(Scale A).<br />
Drawing the appropriate line on the nomogram<br />
4<br />
4<br />
gives an intersection point on Scale B, which<br />
indicates that a 406 x 127 x 254mm valley gutter<br />
and 150mm diameter rainwater pipes are required.<br />
As the valley is 36mm long, three 150mm diameter<br />
rainwater pipes are required. (i.e. 36 ÷ 12).<br />
Meters<br />
3<br />
Gutter length drained<br />
by one rainwater pipe<br />
Rainwater pipe<br />
Gutter<br />
Meters<br />
3<br />
Upslope length<br />
(two slopes at valleys)<br />
Fig.1 Gutter size/roof length nomogram<br />
66 <strong>Profiled</strong> sheeting design guide