NBN Co Network Design Rules
NBN Co Network Design Rules
NBN Co Network Design Rules
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>NBN</strong> <strong>Co</strong> <strong>Network</strong> <strong>Design</strong> <strong>Rules</strong><br />
3.6 Transport Domain<br />
1.1.19. Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM)<br />
The <strong>NBN</strong> <strong>Co</strong> Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) fibre optic transport network is made<br />
up of a number of DWDM Nodes (DNs) situated mainly at Point of Interconnect (POI) and Fibre<br />
Access Node (FAN) sites, all interconnected by Optical Multiplex Section (OMS) links. A DN may also<br />
be used within a link for amplification.<br />
The DWDM network will predominantly provide physical connectivity and transit backhaul capacity<br />
between POI and FAN sites. The network will also provide connectivity to centralised depots, data<br />
centres and delivery points for the specific transport services that require them.<br />
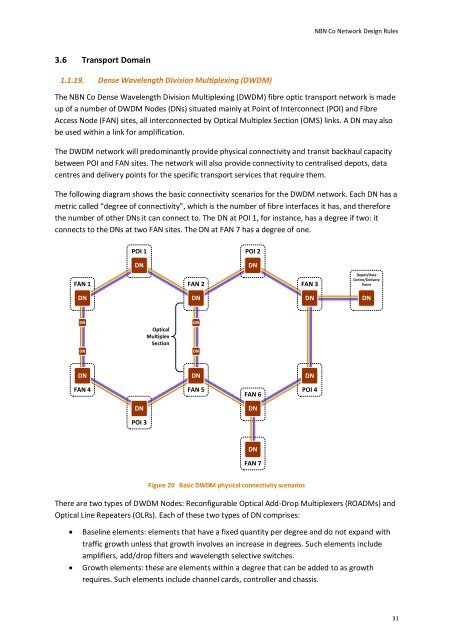
The following diagram shows the basic connectivity scenarios for the DWDM network. Each DN has a<br />
metric called “degree of connectivity”, which is the number of fibre interfaces it has, and therefore<br />
the number of other DNs it can connect to. The DN at POI 1, for instance, has a degree if two: it<br />
connects to the DNs at two FAN sites. The DN at FAN 7 has a degree of one.<br />
POI 1 POI 2<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
FAN 1 FAN 2<br />
FAN 3<br />
Depot/Data<br />
Centre/Delivery<br />
Point<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
Optical<br />
Multiplex<br />
Section<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
FAN 4<br />
FAN 5<br />
FAN 6<br />
POI 4<br />
DN<br />
DN<br />
POI 3<br />
DN<br />
FAN 7<br />
Figure 20 Basic DWDM physical connectivity scenarios<br />
There are two types of DWDM Nodes: Reconfigurable Optical Add-Drop Multiplexers (ROADMs) and<br />
Optical Line Repeaters (OLRs). Each of these two types of DN comprises:<br />
<br />
<br />
Baseline elements: elements that have a fixed quantity per degree and do not expand with<br />
traffic growth unless that growth involves an increase in degrees. Such elements include<br />
amplifiers, add/drop filters and wavelength selective switches.<br />
Growth elements: these are elements within a degree that can be added to as growth<br />
requires. Such elements include channel cards, controller and chassis.<br />
31