NBN Co Network Design Rules
NBN Co Network Design Rules
NBN Co Network Design Rules
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>NBN</strong> <strong>Co</strong> <strong>Network</strong> <strong>Design</strong> <strong>Rules</strong><br />
The EAS offers redundant connectivity to the access domains via 1Gbps, 10Gbps or sub-rate bit<br />
rates. The links can use any of the Transport Domain solutions for connectivity to remote locations<br />
(e.g. FAN sites), or direct fibre for any local connections within the POI (e.g. the PDN-GW for wireless<br />
access).<br />
1.1.23. Ethernet Fanout Switch (EFS)<br />
This platform is used to aggregate a number of Access Seeker interfaces (on the External <strong>Network</strong>-<br />
<strong>Network</strong> Interface, E-NNI) and fan out the traffic towards other Aggregation Domain network<br />
elements such as the Ethernet Aggregation Switch, or another EFS. To support E-NNI redundancy,<br />
EFS are deployed in pairs.<br />
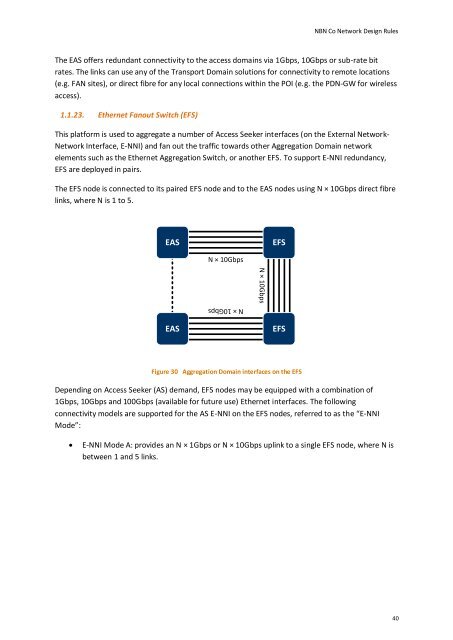
The EFS node is connected to its paired EFS node and to the EAS nodes using N × 10Gbps direct fibre<br />
links, where N is 1 to 5.<br />
EAS<br />
EFS<br />
N × 10Gbps<br />
N × 10Gbps<br />
EAS<br />
N × 10Gbps<br />
EFS<br />
Figure 30 Aggregation Domain interfaces on the EFS<br />
Depending on Access Seeker (AS) demand, EFS nodes may be equipped with a combination of<br />
1Gbps, 10Gbps and 100Gbps (available for future use) Ethernet interfaces. The following<br />
connectivity models are supported for the AS E-NNI on the EFS nodes, referred to as the “E-NNI<br />
Mode”:<br />
<br />
E-NNI Mode A: provides an N × 1Gbps or N × 10Gbps uplink to a single EFS node, where N is<br />
between 1 and 5 links.<br />
40