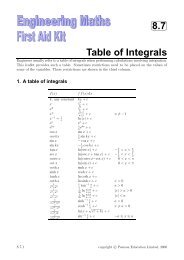
Polynomial functions
Polynomial functions
Polynomial functions
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
3. Write down one example of each of the following types of polynomial function:<br />
(a) cubic (b) linear (c) quartic (d) quadratic<br />
4. Sketch the graphs of the following <strong>functions</strong> on the same axes:<br />
(a) f(x) = x 2 (b) f(x) = 4x 2 (c) f(x) = −x 2 (d) f(x) = −4x 2<br />
5. Consider a function of the form f(x) = x 2 +ax, where a represents a real number. The graph<br />
of this function is represented by a parabola.<br />
(a) When a > 0, what happens to the parabola as a increases?<br />
(b) When a < 0, what happens to the parabola as a decreases?<br />
6. Write down the maximum number of turning points on the graph of a polynomial function<br />
of degree:<br />
(a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 12 (d) n<br />
7. Write down a polynomial function with roots:<br />
(a) 1, 2, 3, 4 (b) 2, −4 (c) 12, −1, −6<br />
8. Write down the roots and identify their multiplicity for each of the following <strong>functions</strong>:<br />
(a) f(x) = (x − 2) 3 (x + 4) 4 (b) f(x) = (x − 1)(x + 2) 2 (x − 4) 3<br />
9. Sketch the following <strong>functions</strong>:<br />
(a) f(x) = (x − 2) 2 (x + 1) (b) f(x) = (x − 1) 2 (x + 3)<br />
Answers<br />
1. A polynomial function is a function that can be written in the form<br />
f(x) = a n x n + a n−1 x n−1 + a n−2 x n−2 + . . . + a 2 x 2 + a 1 x + a 0 ,<br />
where each a 0 , a 1 , etc. represents a real number, and where n is a natural number (including<br />
0).<br />
2.<br />
(a) f(x) = 4x 2 + 2 is a polynomial<br />
(b) f(x) = 3x 3 − 2x + √ x is not a polynomial, because of √ x<br />
(c) f(x) = 12 − 4x 5 + 3x 2 is a polynomial<br />
(d) f(x) = sin x + 1 is not a polynomial, because of sinx<br />
(e) f(x) = 3x 12 − 2/x is not a polynomial, because of 2/x<br />
(f) f(x) = 3x 11 − 2x 12 is a polynomial<br />
3.<br />
(a) The highest power of x must be 3, so examples might be f(x) = x 3 − 2x + 1 or f(x) =<br />
x 3 − 2.<br />
(b) The highest power of x must be 1, so examples might be f(x) = x or f(x) = 6x − 5.<br />
(c) The highest power of x must be 4, so examples might be f(x) = x 4 − 3x 3 + 2x or<br />
f(x) = x 4 − x − 5.<br />
(d) The highest power of x must be 2, so examples might be f(x) = x 2 or f(x) = x 2 − 5.<br />
4.<br />
9 c○ mathcentre July 18, 2005