CANADIAN MEDICAL DEVICES INDUSTRY - LifeSciences BC
CANADIAN MEDICAL DEVICES INDUSTRY - LifeSciences BC
CANADIAN MEDICAL DEVICES INDUSTRY - LifeSciences BC
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Canadian Technology Strength Supports<br />
Innovation<br />
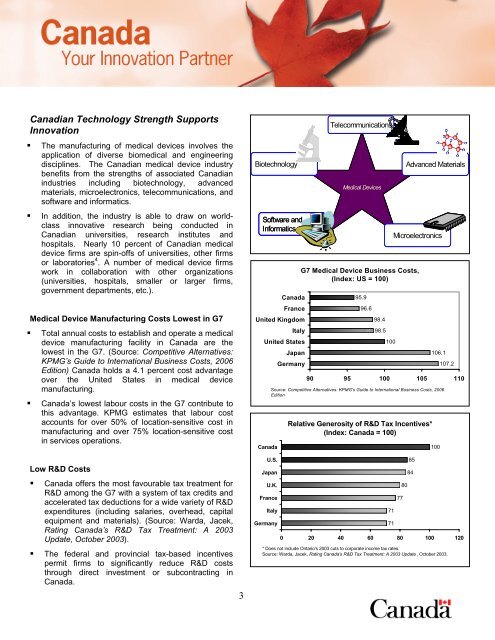
• The manufacturing of medical devices involves the<br />
application of diverse biomedical and engineering<br />
disciplines. The Canadian medical device industry<br />
benefits from the strengths of associated Canadian<br />
industries including biotechnology, advanced<br />
materials, microelectronics, telecommunications, and<br />
software and informatics.<br />
• In addition, the industry is able to draw on worldclass<br />
innovative research being conducted in<br />
Canadian universities, research institutes and<br />
hospitals. Nearly 10 percent of Canadian medical<br />
device firms are spin-offs of universities, other firms<br />
or laboratories 4 . A number of medical device firms<br />
work in collaboration with other organizations<br />
(universities, hospitals, smaller or larger firms,<br />
government departments, etc.).<br />
Medical Device Manufacturing Costs Lowest in G7<br />
• Total annual costs to establish and operate a medical<br />
device manufacturing facility in Canada are the<br />
lowest in the G7. (Source: Competitive Alternatives:<br />
KPMG’s Guide to International Business Costs, 2006<br />
Edition) Canada holds a 4.1 percent cost advantage<br />
over the United States in medical device<br />
manufacturing.<br />
• Canada’s lowest labour costs in the G7 contribute to<br />
this advantage. KPMG estimates that labour cost<br />
accounts for over 50% of location-sensitive cost in<br />
manufacturing and over 75% location-sensitive cost<br />
in services operations.<br />
Low R&D Costs<br />
• Canada offers the most favourable tax treatment for<br />
R&D among the G7 with a system of tax credits and<br />
accelerated tax deductions for a wide variety of R&D<br />
expenditures (including salaries, overhead, capital<br />
equipment and materials). (Source: Warda, Jacek,<br />
Rating Canada’s R&D Tax Treatment: A 2003<br />
Update, October 2003).<br />
• The federal and provincial tax-based incentives<br />
permit firms to significantly reduce R&D costs<br />
through direct investment or subcontracting in<br />
Canada.<br />
3<br />
Biotechnology<br />
Software and<br />
Informatics<br />
United Kingdom<br />
United States<br />
Canada<br />
Canada<br />
France<br />
Italy<br />
Japan<br />
Germany<br />
Telecommunications<br />
Medical Devices<br />
Advanced Materials<br />
Microelectronics<br />
G7 Medical Device Business Costs,<br />
(Index: US = 100)<br />
95.9<br />
96.6<br />
98.4<br />
98.5<br />
100<br />
106.1<br />
107.2<br />
90 95 100 105 110<br />
Source: Competitive Alternatives: KPMG's Guide to International Business Costs, 2006<br />
Edition<br />
U.S.<br />
Japan<br />
U.K.<br />
France<br />
Italy<br />
Germany<br />
Relative Generosity of R&D Tax Incentives*<br />
(Index: Canada = 100)<br />
0 20 40 60 80 100 120<br />
* Does not include Ontario's 2003 cuts to corporate income tax rates.<br />
Source: Warda, Jacek, Rating Canada's R&D Tax Treatment: A 2003 Update , October 2003.<br />
71<br />
71<br />
77<br />
80<br />
85<br />
84<br />
100