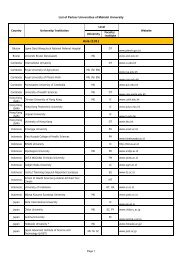
Volume 15 Number 1 - Mahidol University
Volume 15 Number 1 - Mahidol University
Volume 15 Number 1 - Mahidol University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Research<br />
Herbal Extracts as Adjunct in Periodontal Therapy<br />
Centella asiatica (Baibuabok – Thai name) and Punica granatum<br />
(Tuptim-Thai name) are medicinal herbs that have been reported to promote<br />
tissue healing. While C. asiatica extract has the property to stimulate collagen<br />
synthesis, tannin containing extract from P. granatum possesses astringent action.<br />
It also has the affinity to bind with collagen and, therefore, has the capacity to<br />
stabilize it. A double-blind clinical study carried out by Assoc. Prof. Pusadee<br />
Yotnuengnit, et al., investigated effects of the combined extracts from C. asiatica<br />
and P. granatum pericarp as a locally delivered adjunct on periodontal healing<br />
following scaling and root planing (SRP) in adult periodontitis patients. An<br />
innovative combined herbal medicament was formulated in the form of<br />
biodegradable chips for subgingival application.<br />
Patients with initial PD (pocket depth: the defect between root surface<br />
and the gum resulting from destruction of the disease, with more depth indicating<br />
more advanced disease.) of 5 to 8 mm. were enrolled in the study. In each<br />
subject, two teeth in three out of the four quadrants were selected as target<br />
teeth and randomized into three different treatment groups. After baseline<br />
examination and SRP on non-target teeth, the target teeth in the test group received<br />
SRP followed by subgingival delivery of the medicated chips, while the placebo<br />
group received SRP plus plain (unmedicated) chips, and the control group received<br />
SRP alone. The total follow-up period was six months.<br />
Baibuabok<br />
Better improvements of PD and AL (Attachment Loss: indicating vertical<br />
dimension of attachment loss between root surface of the tooth and the gum at<br />
particular site, with a higher value indicating more advanced disease) in the test<br />
group were detected at both 3 and 6 months. The differences reached significant<br />
levels at 3 months when compared with the placebo group. At 6 months, the test<br />
Tuptim<br />
group showed significant overall PD reduction compared to both placebo and<br />
control groups as well as significant improvement in AL. These differences were even more pronounced among the pockets<br />
with initial PD of 7 to 8 mm. All treatment groups exhibited a similar trend of oral hygiene improvement. The test group,<br />
however, showed less percentage of non-bleeding sites. In all treatment groups, mean PD at 3 and 6 months were found to be<br />
statistically lower from baseline. The effect on PD reduction by SRP in this study is, therefore, in agreement with findings from<br />
other reports in respect to improvement of the periodontal condition obtained following supra- and subgingival debridement. This<br />
confirms the effectiveness of SRP as having been used as the “gold standard” therapy.<br />
When changes in PD and AL are taken into consideration, the test group showed quite impressive effects on PD<br />
reduction. This enhancing effect could result from the astringent property of the tannin containing Punica extract in the medicated<br />
chips. The astringent action is usually accompanied by contraction and wrinkling of the tissue. Local edema, inflammation as<br />
well as exudation are also reduced. As tissue shrinkage naturally occurs after SRP, the additional PD reduction observed in the<br />
SRP+med chip group seemed most likely to be facilitated by the characteristic astringency. On the other hand, the augmenting<br />
effect on AL improvement in the test group could be postulated as a result, at least partially, from the stimulatory property of<br />
Centella asiatica as the extract has been known to increase collagen synthesis. While the investigation focused on examining<br />
the enhancing effects of the combined herbal medicament, the overall results obtained could benefit from some other properties<br />
of C. asiatica and P. granatum. These may include antibacterial activities of both the herbs against some microorganisms and<br />
the enzyme inhibitory properties of tannins contained in the Punica extract.<br />
The study concluded that with the use of the newly formulated adjunctive herbal medicament, periodontal healing was<br />
superiorly augmented following conventional periodontal therapy in the test group as compared to the placebo and control<br />
groups. This may provide a new alternative to the use of adjunctive antibiotics which often induces development of bacterial<br />
resistance, and reduces the need for periodontal surgery. Although the preliminary results from this clinical study appear quite<br />
promising, further investigations are required to explain possible mechanisms responsible for the effects of these medicinal<br />
herbs on periodontal healing.<br />
10<br />
SPECTRUM<br />
MAHIDOL UNIVERSITY