Provider Purchasing and Contracting for Health Services_The Case
Provider Purchasing and Contracting for Health Services_The Case
Provider Purchasing and Contracting for Health Services_The Case
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
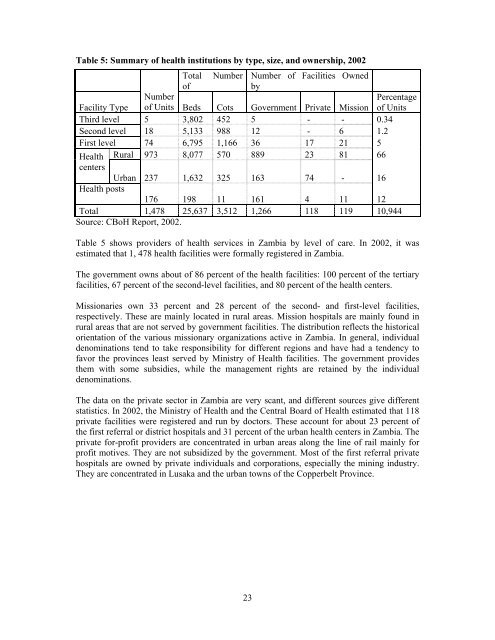
Table 5: Summary of health institutions by type, size, <strong>and</strong> ownership, 2002<br />
Total Number Number of Facilities Owned<br />
of<br />
by<br />
Facility Type<br />
Number<br />
of Units Beds Cots Government Private Mission<br />
Percentage<br />
of Units<br />
Third level 5 3,802 452 5 - - 0.34<br />
Second level 18 5,133 988 12 - 6 1.2<br />
First level 74 6,795 1,166 36 17 21 5<br />
Rural 973 8,077 570 889 23 81 66<br />
<strong>Health</strong><br />
centers<br />
Urban 237 1,632 325 163 74 - 16<br />
<strong>Health</strong> posts<br />
176 198 11 161 4 11 12<br />
Total 1,478 25,637 3,512 1,266 118 119 10,944<br />
Source: CBoH Report, 2002.<br />
Table 5 shows providers of health services in Zambia by level of care. In 2002, it was<br />
estimated that 1, 478 health facilities were <strong>for</strong>mally registered in Zambia.<br />
<strong>The</strong> government owns about of 86 percent of the health facilities: 100 percent of the tertiary<br />
facilities, 67 percent of the second-level facilities, <strong>and</strong> 80 percent of the health centers.<br />
Missionaries own 33 percent <strong>and</strong> 28 percent of the second- <strong>and</strong> first-level facilities,<br />
respectively. <strong>The</strong>se are mainly located in rural areas. Mission hospitals are mainly found in<br />
rural areas that are not served by government facilities. <strong>The</strong> distribution reflects the historical<br />
orientation of the various missionary organizations active in Zambia. In general, individual<br />
denominations tend to take responsibility <strong>for</strong> different regions <strong>and</strong> have had a tendency to<br />
favor the provinces least served by Ministry of <strong>Health</strong> facilities. <strong>The</strong> government provides<br />
them with some subsidies, while the management rights are retained by the individual<br />
denominations.<br />
<strong>The</strong> data on the private sector in Zambia are very scant, <strong>and</strong> different sources give different<br />
statistics. In 2002, the Ministry of <strong>Health</strong> <strong>and</strong> the Central Board of <strong>Health</strong> estimated that 118<br />
private facilities were registered <strong>and</strong> run by doctors. <strong>The</strong>se account <strong>for</strong> about 23 percent of<br />
the first referral or district hospitals <strong>and</strong> 31 percent of the urban health centers in Zambia. <strong>The</strong><br />
private <strong>for</strong>-profit providers are concentrated in urban areas along the line of rail mainly <strong>for</strong><br />
profit motives. <strong>The</strong>y are not subsidized by the government. Most of the first referral private<br />
hospitals are owned by private individuals <strong>and</strong> corporations, especially the mining industry.<br />
<strong>The</strong>y are concentrated in Lusaka <strong>and</strong> the urban towns of the Copperbelt Province.<br />
23