WISC IV INTERPRETIVE WORKSHEET STEP 1 FSIQ ...
WISC IV INTERPRETIVE WORKSHEET STEP 1 FSIQ ...
WISC IV INTERPRETIVE WORKSHEET STEP 1 FSIQ ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
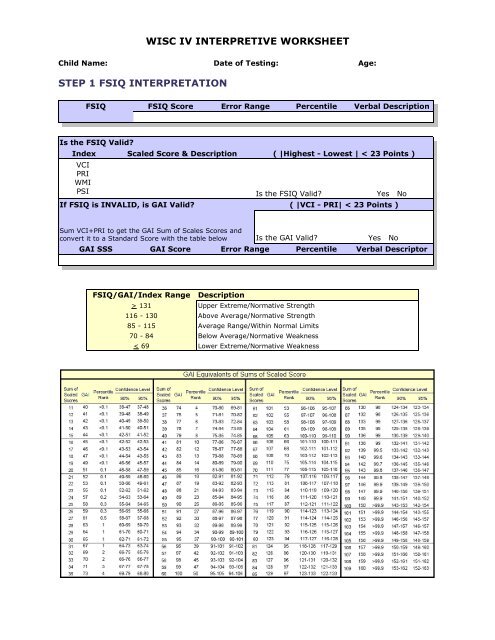
<strong>WISC</strong> <strong>IV</strong> INTERPRET<strong>IV</strong>E <strong>WORKSHEET</strong><br />
Child Name: Date of Testing: Age:<br />
<strong>STEP</strong> 1 <strong>FSIQ</strong> INTERPRETATION<br />
<strong>FSIQ</strong> <strong>FSIQ</strong> Score Error Range Percentile Verbal Description<br />
Is the <strong>FSIQ</strong> Valid?<br />
Index Scaled Score & Description ( |Highest - Lowest | < 23 Points )<br />
VCI<br />
PRI<br />
WMI<br />
PSI Is the <strong>FSIQ</strong> Valid? Yes No<br />
If <strong>FSIQ</strong> is INVALID, is GAI Valid?<br />
( |VCI - PRI| < 23 Points )<br />
Sum VCI+PRI to get the GAI Sum of Scales Scores and<br />
convert it to a Standard Score with the table below<br />
Is the GAI Valid?<br />
Yes No<br />
GAI SSS GAI Score Error Range Percentile Verbal Descriptor<br />
<strong>FSIQ</strong>/GAI/Index Range Description<br />
> 131 Upper Extreme/Normative Strength<br />
116 - 130 Above Average/Normative Strength<br />
85 - 115 Average Range/Within Normal Limits<br />
70 - 84 Below Average/Normative Weakness<br />
< 69 Lower Extreme/Normative Weakness
<strong>STEP</strong> 2 INDEX INTERPRETATION<br />
Are the indexes unitary?<br />
Index<br />
VCI<br />
PRI<br />
WMI<br />
PSI<br />
Highest<br />
Subscale<br />
Lowest<br />
Subscale<br />
Difference<br />
Unitary?<br />
(< 5 points)<br />
Yes No<br />
Yes No<br />
Yes No<br />
Yes No<br />
All subscales < 8 or NW?<br />
All subscales > 12 or NS?<br />
---For Unitary Indexes Only---<br />
Index Index Score Average Index Score Client Difference<br />
VCI<br />
PRI<br />
WMI<br />
PSI<br />
Sum of All Four Indexes = ÷ 4 =<br />
Index<br />
VCI<br />
PRI<br />
WMI<br />
PSI<br />
Client<br />
Difference<br />
Difference<br />
Required for<br />
Significance 1<br />
Difference<br />
Required to be<br />
Uncommon 2<br />
14.0<br />
13.5<br />
15.0<br />
17.0<br />
Personal Strength<br />
or Weakness?<br />
Uncommon?<br />
S W NA U<br />
S W NA U<br />
S W NA U<br />
S W NA U<br />
Descriptor 3<br />
LE BA WNL AA UE<br />
LE BA WNL AA UE<br />
LE BA WNL AA UE<br />
LE BA WNL AA UE<br />
1 Based on age from the table below<br />
2 Uncommon Differences all occur at the 10% or less frequency level<br />
3 See <strong>FSIQ</strong>/GAI/Index Range Table on Page 1<br />
Differences Required for .05 Level Significance by Age<br />
Age VCI PRI WMI PSI Age VCI PRI WMI PSI<br />
6 7.9 7.9 7.6 9.8 12 6.1 6.8 6.8 8.0<br />
7 7.7 7.7 8.2 10.3 13 6.6 6.9 7.5 8.1<br />
8 7.3 7.1 7.6 8.4 14 6.2 7.2 6.9 8.0<br />
9 7.1 10.9 7.7 8.5 15 6.2 7.2 7.2 7.7<br />
10 7.1 10.9 7.7 8.2 16 6.2 7.5 6.9 8.0<br />
11 6.9 6.9 7.2 7.8<br />
Based on Table 4.3 in Flanagan and Kaufman
<strong>STEP</strong> 3 - SUBTEST DISCREPANCIES<br />
Sattler still suggests comparing subtests to either the <strong>FSIQ</strong> mean, or the VCI and PRI mean to<br />
determine a child's personal strengths and weaknesses<br />
Subscale Score Mean<br />
Score<br />
Client<br />
Difference<br />
Difference Required<br />
for Significance 1 2<br />
Strength<br />
Weakness<br />
Uncommon<br />
Similarities (3) S W U<br />
Vocabulary (3) S W U<br />
Comprehension (3) S W U<br />
(Information)<br />
(Word Reasoning)<br />
S W U<br />
S W U<br />
Block Design (4) S W U<br />
Picture Concepts (4) S W U<br />
Matrix Reasoning (3) S W U<br />
(Picture Completion)<br />
S W U<br />
Digit Span (4) S W U<br />
Letter Number (4) S W U<br />
(Arithmetic)<br />
S W U<br />
Coding (4) S W U<br />
Symbol Search (4) S W U<br />
(Cancellation)<br />
Mean Used: VCI and PRI Mean <strong>FSIQ</strong> Mean<br />
S W U<br />
1 Table below includes Difference Required for Significance from whole sample<br />
2 Numbers in parenthesis are seen in 10% or less of the sample<br />
Difference Required for Significance at .05 Level<br />
Subtest Mean of 3<br />
Index Subtests<br />
Mean of 4<br />
Index Subtests<br />
Mean of 5<br />
Index Subtests<br />
Mean of 15<br />
Subtests<br />
Similarities 2.23 2.46 2.65 3.22<br />
Vocabulary 2.11 2.28 2.43 3.22<br />
Comprehension 2.41 2.73 2.96 3.06<br />
(Information) 2.51 2.70 3.64<br />
(Word Reasoning) 2.81 3.01 3.40<br />
Block Design 2.22 2.47 2.88<br />
Picture Concepts 2.38 2.70 2.80<br />
Matrix Reasoning 2.09 2.27 2.85<br />
(Picture Completion) 2.57 3.70<br />
Digit Span 2.05 3.83<br />
Letter Number 1.95 3.40<br />
(Arithmetic) 2.03 3.88<br />
Coding 2.46 3.30<br />
Symbol Search 2.61 3.01<br />
(Cancellation) 2.63 3.78
Flanagan and Kaufman's Planned Comparisons<br />
Cluster 1 Cluster 2 Actual<br />
Difference<br />
Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Sum Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Standard<br />
Scores*<br />
Gf<br />
MR PCn A<br />
Gv<br />
BD PCm<br />
When Gf (Fluid Reasoning) is higher, it may<br />
indicate the child has good verbal reasoning ability<br />
and can solve problems most easily when they are<br />
able to translate visual into verbal material<br />
Difference Required to<br />
be Uncommon<br />
Strength?<br />
Are These Unitary Factors? (< 5 points)<br />
Gf highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
Gv highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
- = Needed - 21 Sig Non<br />
When Gv (Visual Reasoning) is higher, it may indicate the<br />
child has good basic visual skills, but difficulty using visual<br />
information, as when making predictions based on charts and<br />
graphs, and integrating visual information to solve a problem<br />
Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Sum Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Standard<br />
Scores*<br />
Gf nonverbal<br />
MR PCn<br />
Gv<br />
BD PCm<br />
When Gf nonverbal (Nonverbal Fluid Reasoning) is<br />
higher, it may indicate that the child may learn<br />
best when new information is organized with<br />
graphics, charts, drawings, etc...<br />
Are These Unitary Factors? (< 5 points)<br />
Gf nonverbal highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
Gv highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
- = Needed - 24 Sig Non<br />
When Gv (Visual Reasoning) is higher, it may indicate that<br />
the child has a good basic visual skills, but has difficulty<br />
using visual information, as when making predictions based<br />
on charts and graphs, and integrating visual information to<br />
solve a problem<br />
Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Sum Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Standard<br />
Scores*<br />
Gf nonverbal<br />
MR PCn<br />
Gf verbal<br />
SI WR<br />
When Gf nonverbal (Nonverbal Fluid Reasoning) is<br />
higher, it may indicate that the child may learn<br />
best when new information is organized with<br />
graphics, charts, drawings, etc...<br />
Are These Unitary Factors? (< 5 points)<br />
Gf nonverbal highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
Gv verbal highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
- = Needed - 24 Sig Non<br />
When Gf verbal (Verbal Fluid Reasoning) is higher, it may<br />
indicate the child can reason most easily with verbally-based<br />
material; they may do well with "lecture format" classes, so<br />
long as they do not include too many pictures, charts, and<br />
graphs<br />
Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Sum Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Standard<br />
Scores*<br />
Gc lexical<br />
WR VO<br />
Gc general<br />
CO IN<br />
When Gc lexical (Crystalized Lexical Knowledge) is<br />
higher, it may indicate that the child can reason<br />
with words, but has limited factual information;<br />
writing may be hard because they know the words<br />
to use, but have little to say, and can read but not<br />
understand important points<br />
Are These Unitary Factors? (< 5 points)<br />
Gc lexical highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
Gc general highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
- = Needed - 17 Sig Non<br />
When Gc general (General Crystalized Knowledge) is higher,<br />
it may indicate that the child has good factual knowledge,<br />
but difficulty with words; this may mean that on writing<br />
assignments, the child knows what to say that does not know<br />
how to say it, and may be able to read and understand<br />
familiar topics but have difficulty with novel material
Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Sum Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Standard<br />
Scores*<br />
Gc LTM<br />
IN VO<br />
Gsm WM<br />
LN DSp<br />
When Glc LTM (Long-Term Memory) is higher, it<br />
may indicate that the child has adequate factual<br />
knowledge through repeated practice with familiar<br />
topics, but when learning new material has<br />
difficulty holding information in short-term<br />
memory long enough to understand the "big<br />
picture"<br />
Are These Unitary Factors? (< 5 points)<br />
Gc LTM highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
Gs WM highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
- = Needed - 24 Sig Non<br />
When Gsm WM (Short-Term Memory or Working Memory) is<br />
higher, it may indicate that the child can learn new<br />
information, but has difficulty recalling it with a delay; others<br />
may say they know information immediately after studying,<br />
but forget it the next day. They likely are not forgetting, but<br />
rather are not learning it in a way that they can later recall<br />
Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Sum Scaled<br />
Scores<br />
Standard<br />
Scores*<br />
Gc LTM<br />
IN VO<br />
Gf verbal<br />
SI WR<br />
When Glc LTM (Long-Term Memory) is higher, it<br />
may indicate that the child has adequate factual<br />
knowledge through repeated practice with familiar<br />
topics, but has difficulty using new information<br />
Are These Unitary Factors? (< 5 points)<br />
Gc LTM highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
Gf verbal highest score - lowest score<br />
Yes No<br />
- = Needed - 17 Sig Non<br />
* See Tables 1 through 8 to convert Sum Scaled Scores into Standard Scores<br />
When Gf verbal (Verbal Fluid Reasoning) is higher, it may<br />
indicate the child can reason most easily with verbally-based<br />
material, but may have little information to reason with<br />
Scaled<br />
Score<br />
1 to 4<br />
5 to 7<br />
Sattler's Suggested Scale Score Descriptors<br />
Description Percentile Scaled Description<br />
Range Score<br />
Exceptional weakness<br />
Very poorly developed<br />
Far below average<br />
Weakness<br />
Poorly developed<br />
Below average<br />
1st to 2nd 13 to 15<br />
5th to 16th 16 to 19<br />
Strength<br />
Well developed<br />
Above average<br />
Exceptional strength<br />
Very well developed<br />
Superior<br />
Percentile<br />
Range<br />
84th to 95th<br />
98th to 99th<br />
8 to 12 Average 25th to 75th<br />
Age<br />
DSpan<br />
Forwards<br />
6-8 5<br />
9-14 6<br />
15-16 7<br />
Average Digits Recalled by Age<br />
Recalled By<br />
DSpan<br />
Backwards<br />
50-75%<br />
3<br />
4<br />
5<br />
%tile<br />
50-75%<br />
R Niolon
Sums of Scaled Scores to Cluster Standard Scores<br />
Table 1 Gf (Fluid Reasoning)<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
3 50 99<br />
15 71 3 29 98 45 43 127 97 57 150 >99<br />
16 73 3 30 100 50 44 129 97<br />
95% Conf = + 8<br />
Table 2 Gv (Visual Reasoning)<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
2 50 99<br />
8 67 1 18 94 35 28 123 93 38 150 >99<br />
9 70 2 19 97 43 29 126 96<br />
10 72 3 20 100 50 30 130 98 95% Conf = + 8<br />
11 75 5 21 103 57 31 133 99<br />
Table 3 Gf nonverbal (Nonverbal Fluid Reasoning)<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
2 50 99<br />
9 69 2 19 97 43 29 127 97<br />
10 71 3 20 100 50 30 130 98<br />
95% Conf = + 8<br />
11 74 4 21 103 57 31 133 99<br />
Table 4 Gf verbal (Verbal Fluid Reasoning)<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
2 50 99<br />
9 69 2 19 97 43 29 126 96<br />
10 72 3 20 100 50 30 129 97<br />
95% Conf = + 8<br />
11 75 5 21 102 55 31 132 98
Table 5 Gc lexical (Crystalized Lexical Knowledge)<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
2 50 99<br />
8 68 2 18 94 35 28 123 93 38 150 >99<br />
9 71 3 19 96 40 29 126 96<br />
10 74 4 20 99 48 30 129 97<br />
95% Conf = + 8<br />
11 76 5 21 102 55 31 132 98<br />
Table 6 Gc general (General Crystalized Knowledge)<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
2 50 99<br />
8 68 2 18 94 35 28 123 93 38 150 >99<br />
9 71 3 19 97 43 29 126 96<br />
10 73 3 20 99 48 30 129 97<br />
95% Conf = + 8<br />
11 76 5 21 102 55 31 131 98<br />
Table 7 Gc LTM (Long-Term Memory/Retrieval)<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
2 50 99<br />
9 72 3 19 97 43 29 125 95<br />
10 74 3 20 99 48 30 127 97<br />
11 77 6 21 102 55 31 130 98<br />
95% Conf = + 8<br />
Table 8 Standard Scores for Gsm WM<br />
SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile SSS Stand %tile<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
Score<br />
2 50 99<br />
9 68 2 19 97 43 29 126 96<br />
10 71 3 20 99 48 30 129 97<br />
11 74 4 21 102 55 31 132 98<br />
95% Conf = + 8