Dampers for Centrifugal Fans - Greenheck
Dampers for Centrifugal Fans - Greenheck
Dampers for Centrifugal Fans - Greenheck
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
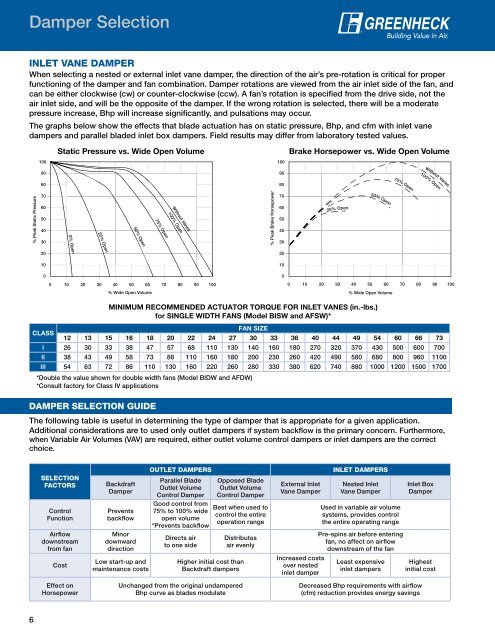
Damper Selection<br />
INLET VANE DAMPER<br />
<br />
functioning of the damper and fan combination. Damper rotations are viewed from the air inlet side of the fan, and<br />
<br />
air inlet side, and will be the opposite of the damper. If the wrong rotation is selected, there will be a moderate<br />
pressure increase, Bhp will increase significantly, and pulsations may occur.<br />
The graphs below show the effects that blade actuation has on static pressure, Bhp, and cfm with inlet vane<br />
<br />
Static Pressure vs. Wide Open Volume<br />
Brake Horsepower vs. Wide Open Volume<br />
100<br />
100<br />
Without Vanes<br />
90<br />
90<br />
80<br />
80<br />
75% Open<br />
100% Open<br />
% Peak Static Pressure<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
50% Open<br />
75% Open<br />
Without Vanes<br />
100% Open<br />
% Peak Brake Horsepower<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
25% Open<br />
50% Open<br />
25% Open<br />
0% Open<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
% Wide Open Volume<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100<br />
% Wide Open Volume<br />
CLASS<br />
MINIMUM RECOMMENDED ACTUATOR TORQUE FOR INLET VANES (in.-lbs.)<br />
<strong>for</strong> SINGLE WIDTH FANS (Model BISW and AFSW)*<br />
<br />
*Consult factory <strong>for</strong> Class IV applications<br />
DAMPER SELECTION GUIDE<br />
FAN SIZE<br />
12 13 15 16 18 20 22 24 27 30 33 36 40 44 49 54 60 66 73<br />
I 26 30 33 38 47 57 68 110 130 140 160 180 270 320 370 430 500 600 700<br />
II 38 43 49 58 73 88 110 160 180 200 230 260 420 490 580 680 800 960 1100<br />
III 54 63 72 86 110 130 160 220 260 280 330 380 620 740 880 1000 1200 1500 1700<br />
The following table is useful in determining the type of damper that is appropriate <strong>for</strong> a given application.<br />
Additional considerations are to used only outlet dampers <br />
when Variable Air Volumes (VAV) are required, either outlet volume control dampers or inlet dampers are the correct<br />
choice.<br />
SELECTION<br />
FACTORS<br />
Control<br />
<br />
Airflow<br />
downstream<br />
from fan<br />
Cost<br />
<br />
Horsepower<br />
Backdraft<br />
Damper<br />
Prevents<br />
backflow<br />
Minor<br />
downward<br />
direction<br />
Low start-up and<br />
maintenance costs<br />
OUTLET DAMPERS<br />
Parallel Blade<br />
Outlet Volume<br />
Control Damper<br />
Good control from<br />
75% to 100% wide<br />
open volume<br />
*Prevents backflow<br />
Directs air<br />
to one side<br />
Opposed Blade<br />
Outlet Volume<br />
Control Damper<br />
Best when used to<br />
control the entire<br />
operation range<br />
Distributes<br />
air evenly<br />
Higher initial cost than<br />
Backdraft dampers<br />
Unchanged from the original undampered<br />
Bhp curve as blades modulate<br />
<br />
Vane Damper<br />
Increased costs<br />
over nested<br />
inlet damper<br />
INLET DAMPERS<br />
<br />
Vane Damper<br />
Used in variable air volume<br />
systems, provides control<br />
the entire operating range<br />
Pre-spins air be<strong>for</strong>e entering<br />
fan, no affect on airflow<br />
downstream of the fan<br />
Least expensive<br />
inlet dampers<br />
Inlet Box<br />
Damper<br />
Highest<br />
initial cost<br />
Decreased Bhp requirements with airflow<br />
(cfm) reduction provides energy savings<br />
6