- Page 2 and 3: Promised Land: Palm Oil and Land Ac
- Page 4 and 5: Acknowledgements The authors would
- Page 6 and 7: Contents Executive Summary 11 Chapt
- Page 8 and 9: Acronyms ADB AMDAL ANDAL APL BAL BA
- Page 10 and 11: SKT SPPT TGHK UN UPSB UPSBM UPSBK U
- Page 12 and 13: mainly so speculators can get acces
- Page 14 and 15: Policies Favour Large-scale Plantat
- Page 16 and 17: In effect the government is failing
- Page 18 and 19: Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Reasons
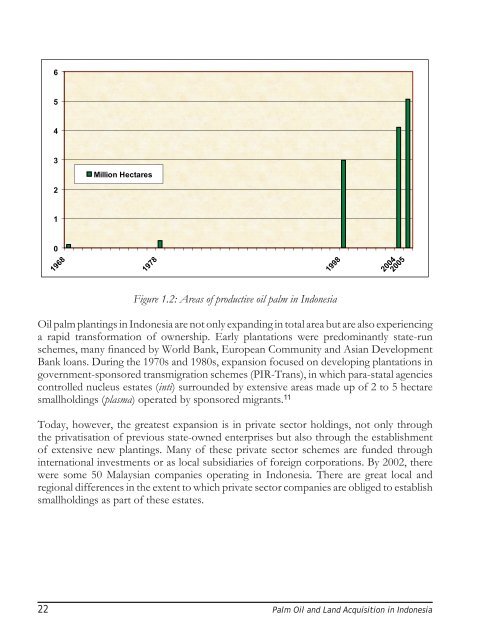
- Page 20 and 21: Notwithstanding these limitations,
- Page 24 and 25: figures, in the past five years, an
- Page 26 and 27: Table 1.2. Provincial Government Pl
- Page 28 and 29: Figure 1.5 Areas of current oil pal
- Page 30 and 31: Endnotes: 1 Foe 2004; Wakker 2004;
- Page 32 and 33: Chapter 2 Towards Responsible Palm
- Page 34 and 35: The 25 persons were selected from a
- Page 36 and 37: Details about negotiated agreements
- Page 38 and 39: A simplified version of the TNC/DfI
- Page 40 and 41: Negotiating acceptable standards fo
- Page 42 and 43: Chapter 3 The Normative Framework -
- Page 44 and 45: 3.2 Government Policy on Palm Oil D
- Page 46 and 47: evaluate proposals for conversion o
- Page 48 and 49: Moreover, although the Act emphasiz
- Page 50 and 51: corresponding customary law communi
- Page 52 and 53: Although the application of this pr
- Page 54 and 55: were part of national development p
- Page 56 and 57: electricity. 52 It is not clear tha
- Page 58 and 59: ISSUANCE PROCEDURE STAGES FOR PLANT
- Page 60 and 61: Translation Section for the table a
- Page 62 and 63: According to the Decree, to obtain
- Page 64 and 65: Article 8 of this decree states tha
- Page 66 and 67: Table 3.1: Indonesian Forest Area b
- Page 68 and 69: option available. The overarching l
- Page 70 and 71: several times the last being Staatb
- Page 72 and 73:
Chapter 4 Case Studies As part of t
- Page 74 and 75:
In the 1990s, the coastal adat comm
- Page 76 and 77:
In the New Order era, communities w
- Page 78 and 79:
project participants, who have not
- Page 80 and 81:
Testimony of Mr. Ajan, from Ngaras,
- Page 82 and 83:
On 10 December 1993, the land offic
- Page 84 and 85:
fact that the compensation being pr
- Page 86 and 87:
Figure 4.2 Map of Kampung & Adat ar
- Page 88 and 89:
Figure 4.3 Map of Plasma & Nucleus
- Page 90 and 91:
6,260 ha. of land in Bengkunat. Lik
- Page 92 and 93:
4.1.6 Land Redistribution: Marga Re
- Page 94 and 95:
international transportation linkin
- Page 96 and 97:
The government of Sanggau district
- Page 98 and 99:
Table 4.4: Land Use of Proposed PT
- Page 100 and 101:
These changes have also had their c
- Page 102 and 103:
4.3 PTPN XIII 4.3.1 Background to P
- Page 104 and 105:
lands were allocated to the company
- Page 106 and 107:
through the required process of lan
- Page 108 and 109:
▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ PTP
- Page 110 and 111:
▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Smallholder fam
- Page 112 and 113:
transmigration uniform, with passio
- Page 114 and 115:
Testimony of a third Transmigrant I
- Page 116 and 117:
widely publicised Decree of the Min
- Page 118 and 119:
The Environmental Impact Assessment
- Page 120 and 121:
Official in the Provincial Regional
- Page 122 and 123:
Mr. Ir. Pontas Sihotang, Head of Pl
- Page 124 and 125:
of executive members. In this situa
- Page 126 and 127:
The company successfully acquired 1
- Page 128 and 129:
Local people strongly rejected the
- Page 130 and 131:
Under the still vigorous customary
- Page 132 and 133:
authority to decide. In some cases,
- Page 134 and 135:
Since 1992, Pasaman District has be
- Page 136 and 137:
Those arrested from Kapar were late
- Page 138 and 139:
Picture 4. Recommendation Letter of
- Page 140 and 141:
▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Land acquisition sh
- Page 142 and 143:
1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) Accept migrants c
- Page 144 and 145:
Picture 6. A letter of ulayat land
- Page 146 and 147:
Local community members of Kapar re
- Page 148 and 149:
4.6.8 A history of Land Disputes in
- Page 150 and 151:
distinct from other community membe
- Page 152 and 153:
not written. The formal validation
- Page 154 and 155:
According to the Head of BPN in Wes
- Page 156 and 157:
Endnotes: 1 LeBar (1972) refers to
- Page 158 and 159:
Mulang Maya (Choiruddin); Village h
- Page 160 and 161:
activist and legal adviser to this
- Page 162 and 163:
Ministry of Industry and Trade, Ria
- Page 164 and 165:
147 In accordance with Law No. 56 o
- Page 166 and 167:
Chapter 5 Legal Analysis Chapter 3
- Page 168 and 169:
5.1.1 Land Ownership As noted, a ba
- Page 170 and 171:
We can see these elements in confli
- Page 172 and 173:
2. The second model is an agreement
- Page 174 and 175:
environmental impacts, could place
- Page 176 and 177:
The Forestry Law (UU Kehutanan): li
- Page 178 and 179:
not have been categorized as State
- Page 180 and 181:
▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ At the stage when a
- Page 182 and 183:
estate labourers, out-growers or di
- Page 184 and 185:
▪ ▪ ▪ Establishment of open a
- Page 186 and 187:
▪ If RSPO adopted lowered standar
- Page 188 and 189:
Boomgard (1998) Between Sovereign D
- Page 190 and 191:
ICBS (1997: 88) Kalimantan Review (
- Page 192 and 193:
Sargent, Howard J (2001) Vegetation
- Page 194 and 195:
Appendix Total 8 Principles and 39
- Page 196 and 197:
promote the positive ones are made,