An automatic fire searching and suppression system for large spaces
An automatic fire searching and suppression system for large spaces
An automatic fire searching and suppression system for large spaces
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
ARTICLE IN PRESS<br />
T. Chen et al. / Fire Safety Journal 39 (2004) 297–307 305<br />
3. Experiment<br />
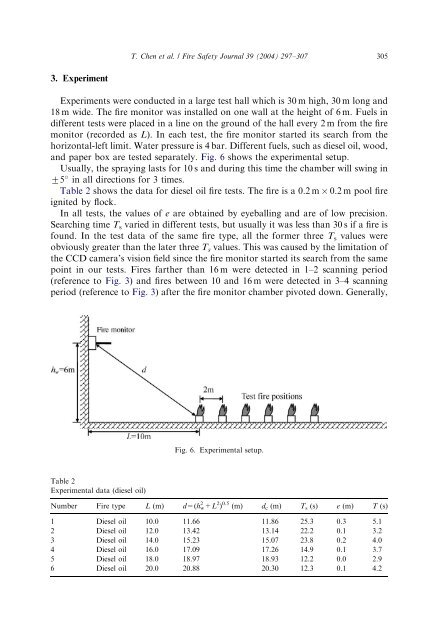
Experiments were conducted in a <strong>large</strong> test hall which is 30 m high, 30 m long <strong>and</strong><br />
18 m wide. The <strong>fire</strong> monitor was installed on one wall at the height of 6 m. Fuels in<br />
different tests were placed in a line on the ground of the hall every 2 m from the <strong>fire</strong><br />
monitor (recorded as L). In each test, the <strong>fire</strong> monitor started its search from the<br />
horizontal-left limit. Water pressure is 4 bar. Different fuels, such as diesel oil, wood,<br />
<strong>and</strong> paper box are tested separately. Fig. 6 shows the experimental setup.<br />
Usually, the spraying lasts <strong>for</strong> 10 s <strong>and</strong> during this time the chamber will swing in<br />
75 in all directions <strong>for</strong> 3 times.<br />
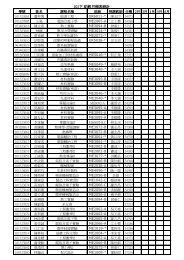
Table 2 shows the data <strong>for</strong> diesel oil <strong>fire</strong> tests. The <strong>fire</strong> is a 0.2 m 0.2 m pool <strong>fire</strong><br />
ignited by flock.<br />
In all tests, the values of e are obtained by eyeballing <strong>and</strong> are of low precision.<br />
Searching time T s varied in different tests, but usually it was less than 30 s if a <strong>fire</strong> is<br />
found. In the test data of the same <strong>fire</strong> type, all the <strong>for</strong>mer three T s values were<br />
obviously greater than the later three T s values. This was caused by the limitation of<br />
the CCD camera’s vision field since the <strong>fire</strong> monitor started its search from the same<br />
point in our tests. Fires farther than 16 m were detected in 1–2 scanning period<br />
(reference to Fig. 3) <strong>and</strong> <strong>fire</strong>s between 10 <strong>and</strong> 16 m were detected in 3–4 scanning<br />
period (reference to Fig. 3) after the <strong>fire</strong> monitor chamber pivoted down. Generally,<br />
Fig. 6. Experimental setup.<br />
Table 2<br />
Experimental data (diesel oil)<br />
Number Fire type L (m) d=(h w 2 +L 2 ) 0.5 (m) d c (m) T s (s) e (m) T (s)<br />
1 Diesel oil 10.0 11.66 11.86 25.3 0.3 5.1<br />
2 Diesel oil 12.0 13.42 13.14 22.2 0.1 3.2<br />
3 Diesel oil 14.0 15.23 15.07 23.8 0.2 4.0<br />
4 Diesel oil 16.0 17.09 17.26 14.9 0.1 3.7<br />
5 Diesel oil 18.0 18.97 18.93 12.2 0.0 2.9<br />
6 Diesel oil 20.0 20.88 20.30 12.3 0.1 4.2