EXOTIC WOODY WEEDS Use of simulation models to predict future ...
EXOTIC WOODY WEEDS Use of simulation models to predict future ...
EXOTIC WOODY WEEDS Use of simulation models to predict future ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
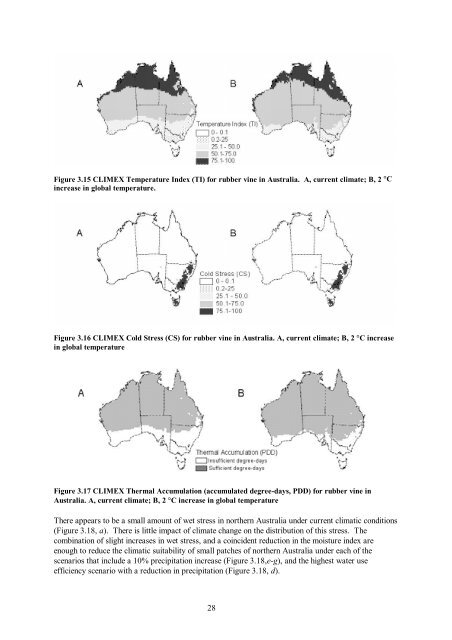
Figure 3.15 CLIMEX Temperature Index (TI) for rubber vine in Australia. A, current climate; B, 2 °C<br />
increase in global temperature.<br />
Figure 3.16 CLIMEX Cold Stress (CS) for rubber vine in Australia. A, current climate; B, 2 °C increase<br />
in global temperature<br />
Figure 3.17 CLIMEX Thermal Accumulation (accumulated degree-days, PDD) for rubber vine in<br />
Australia. A, current climate; B, 2 °C increase in global temperature<br />
There appears <strong>to</strong> be a small amount <strong>of</strong> wet stress in northern Australia under current climatic conditions<br />
(Figure 3.18, a). There is little impact <strong>of</strong> climate change on the distribution <strong>of</strong> this stress. The<br />
combination <strong>of</strong> slight increases in wet stress, and a coincident reduction in the moisture index are<br />
enough <strong>to</strong> reduce the climatic suitability <strong>of</strong> small patches <strong>of</strong> northern Australia under each <strong>of</strong> the<br />
scenarios that include a 10% precipitation increase (Figure 3.18,e-g), and the highest water use<br />
efficiency scenario with a reduction in precipitation (Figure 3.18, d).<br />
28