Lines, Curves and Surfaces in 3D
Lines, Curves and Surfaces in 3D
Lines, Curves and Surfaces in 3D
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
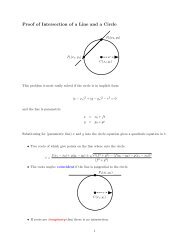
Polygons (Cont.)<br />
P 3 (x 3 ,y 3 )<br />
P 2 (x 2 ,y 2 )<br />
P 6 (x 6 ,y 6 )<br />
P 4 (x 4 ,y 4 )<br />
e 2<br />
e 3<br />
e 1<br />
e 6<br />
e 7<br />
P 1 (x 1 ,y 1 ) P 7 (x 7 ,y 7 )<br />
e 5 e 4<br />
P 5 (x 5 ,y 5 )<br />
• Each l<strong>in</strong>e is def<strong>in</strong>ed by two vertices — the start <strong>and</strong> end po<strong>in</strong>ts.<br />
• We can def<strong>in</strong>e a data structure which stores a list of po<strong>in</strong>ts<br />
(coord<strong>in</strong>ate positions) <strong>and</strong> the edges def<strong>in</strong>e by <strong>in</strong>dexes to two<br />
po<strong>in</strong>ts:<br />
Po<strong>in</strong>ts : {P 1 (x 1 , y 1 ), P 2 (x 2 , y 2 ), P 3 (x 3 , y 3 ), . . .}<br />
Po<strong>in</strong>ts def<strong>in</strong>e the geometry of the polygon.<br />
Edges : Edges : {e 1 = (P 1 , P 2 ), e 2 = (P 2 , P 3 ), . . .<br />
Edges def<strong>in</strong>e the topology of the polygon.<br />
• If you traverse the polygon po<strong>in</strong>ts <strong>in</strong> an ordered direction<br />
(clockwise) then the l<strong>in</strong>es def<strong>in</strong>e a closed shape with the <strong>in</strong>side<br />
on the right of each l<strong>in</strong>e.<br />
CM0268<br />
MATLAB<br />
DSP<br />
GRAPHICS<br />
542<br />
1<br />
◭◭<br />
◮◮<br />
◭<br />
◮<br />
Back<br />
Close