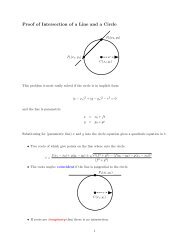
Lines, Curves and Surfaces in 3D
Lines, Curves and Surfaces in 3D
Lines, Curves and Surfaces in 3D
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Compound Geometric Transformations<br />
It is a simple task to create compound transformations (e.g. A rotation<br />
followed by a translation:<br />
• Perform Matrix-Matrix multiplications, e.g. T.R θ<br />
– Note <strong>in</strong> general T.R θ ≠ R θ .T (Basic non-commutative law of<br />
multiplication)<br />
• One problem exists <strong>in</strong> that a 2D Translation cannot be represented<br />
as a 2D matrix — it must be represented a <strong>3D</strong> matrix:<br />
⎛ ⎞<br />
1 0 dx<br />
T = ⎝ 0 1 dy ⎠<br />
0 0 1<br />
( )<br />
cos θ s<strong>in</strong> θ<br />
• So how do we comb<strong>in</strong>e a 2D rotation R θ . =<br />
− s<strong>in</strong> θ cos θ<br />
with a translation<br />
We need to def<strong>in</strong>e Homogeneous Coord<strong>in</strong>ates to deal with this<br />
issue.<br />
CM0268<br />
MATLAB<br />
DSP<br />
GRAPHICS<br />
548<br />
1<br />
◭◭<br />
◮◮<br />
◭<br />
◮<br />
Back<br />
Close