AME 436
AME 436
AME 436
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
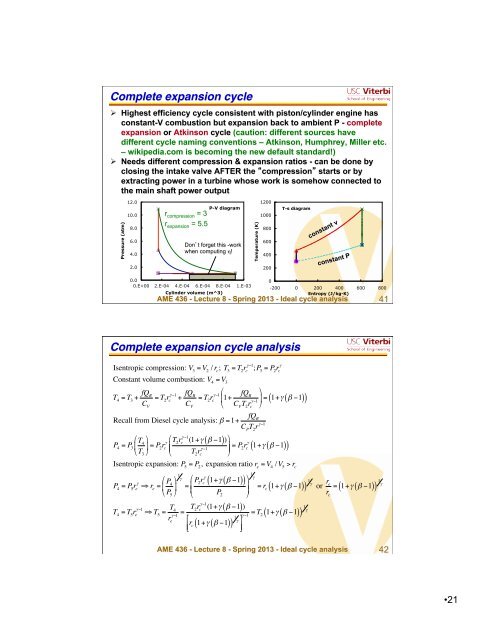
Complete expansion cycle"<br />
Highest efficiency cycle consistent with piston/cylinder engine has<br />
constant-V combustion but expansion back to ambient P - complete<br />
expansion or Atkinson cycle (caution: different sources have<br />
different cycle naming conventions – Atkinson, Humphrey, Miller etc.<br />
– wikipedia.com is becoming the new default standard!)<br />
Needs different compression & expansion ratios - can be done by<br />
closing the intake valve AFTER the compression starts or by<br />
extracting power in a turbine whose work is somehow connected to<br />
the main shaft power output<br />
Pressure (atm)<br />
Pressure (atm)<br />
Compression Combustion Expansion<br />
Blowdown Compression Intake Combustion Exhaust Expansion<br />
Intake Blowdown start 1 Intake 2 Exhaust<br />
3 Intake start 4 1 5 2<br />
6 3 7 4 5<br />
12.0<br />
12.0<br />
6 7<br />
P-V diagram<br />
P-V diagram<br />
10.0<br />
10.0<br />
8.0<br />
8.0<br />
6.0<br />
6.0<br />
4.0<br />
4.0<br />
2.0<br />
2.0<br />
0.0<br />
0.0<br />
0.E+00 2.E-04 4.E-04 6.E-04 8.E-04 1.E-03<br />
0.E+00 2.E-04 4.E-04 6.E-04 8.E-04<br />
Cylinder volume (m^3)<br />
1.E-03<br />
Cylinder volume (m^3)<br />
1200<br />
r compression = 3<br />
r expansion = 5.5<br />
Dont forget this -work<br />
when computing η!<br />
T-s diagram<br />
Compression Combustion Expansion<br />
Blowdown<br />
Close T-s cycle<br />
Temperature (K)<br />
Compression Combustion Expansion<br />
Blowdown Intake Exhaust<br />
Close T-s cycle 1 2<br />
3 4 5<br />
6 7<br />
1200<br />
T-s diagram<br />
1000<br />
800<br />
600<br />
400<br />
200<br />
0<br />
constant v<br />
constant P<br />
-200 0 200 400 600 800<br />
Entropy (J/kg-K)<br />
<strong>AME</strong> <strong>436</strong> - Lecture 8 - Spring 2013 - Ideal cycle analysis<br />
41<br />
1000<br />
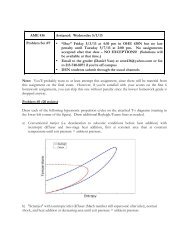
Complete expansion cycle analysis"<br />
Temperature (K)<br />
800<br />
Isentropic compression: V 3<br />
= V 2<br />
/ r c<br />
; T 3<br />
= T 2<br />
r c !!1 ;P 3<br />
= P 2<br />
r c<br />
!<br />
600<br />
Constant volume combustion: V 4<br />
= V 3<br />
400<br />
T 4<br />
= T 3<br />
+ fQ R<br />
= T 2<br />
r !!1 c<br />
+ fQ "<br />
R<br />
= T 2<br />
r !!1 fQ<br />
c<br />
1+ R<br />
%<br />
$<br />
!!1<br />
' = 1+! " !1<br />
C V # C V<br />
T 2<br />
r c &<br />
200 C V<br />
Recall from Diesel cycle analysis: " =1+<br />
fQ R<br />
0<br />
-100 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700<br />
Entropy (J/kg-K)<br />
C P<br />
T 2<br />
r !!1<br />
" T<br />
P 4<br />
= P 4<br />
%<br />
3 $<br />
# T 3 &<br />
' = P r " T r !!1 (1+! ( " !1 ))%<br />
! 2 c<br />
2 c $<br />
!!1<br />
# T 2<br />
r<br />
'<br />
c &<br />
= P !<br />
2r c<br />
( ( ))<br />
( 1+! (" !1))<br />
Isentropic expansion: P 5<br />
= P 2<br />
, expansion ratio r e<br />
= V 4<br />
/V 5<br />
> r c<br />
( ( ))<br />
1 !<br />
= r c ( 1+! (" !1)) 1 !<br />
or r e<br />
P 4<br />
= P 5<br />
r ! e<br />
( r e<br />
= P 1<br />
" % ! "<br />
4<br />
$ ' = P !<br />
2r c<br />
1+! " !1 %<br />
# P 5 &<br />
$<br />
# P '<br />
2 &<br />
T 4<br />
= T 5<br />
r !!1 e<br />
( T 5<br />
= T 4<br />
r = T 2r !!1 c<br />
(1+! (" !1))<br />
!!1<br />
e )<br />
r c ( 1+! (" !1)) 1 ! ,<br />
= T !!1 2<br />
1+! " !1<br />
*+<br />
-.<br />
( ( )) 1 !<br />
( ( )) 1 !<br />
r c<br />
= 1+! " !1<br />
<strong>AME</strong> <strong>436</strong> - Lecture 8 - Spring 2013 - Ideal cycle analysis<br />
42<br />
• 21