did you know?
did you know?
did you know?
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
six stages of visual perception<br />
>>key <strong>know</strong>ledge>><br />
Application of psychological perspectives to explain<br />
visual perception:<br />
> characteristics of the visual perceptual system and<br />
the visual processes involved in detecting and<br />
interpreting visual stimuli<br />
> the effect of psychological factors on perceptual set<br />
> distortions of visual perceptions by illusions.<br />
(VCE Study Design 2009)<br />
A study of the way in which we perceive the world around<br />
us through the sense of vision is a wonderful example of the<br />
way the brain and body work together, depend on each other<br />
and help each other as we go about our everyday activities.<br />
One of the key objectives of this chapter is to help<br />
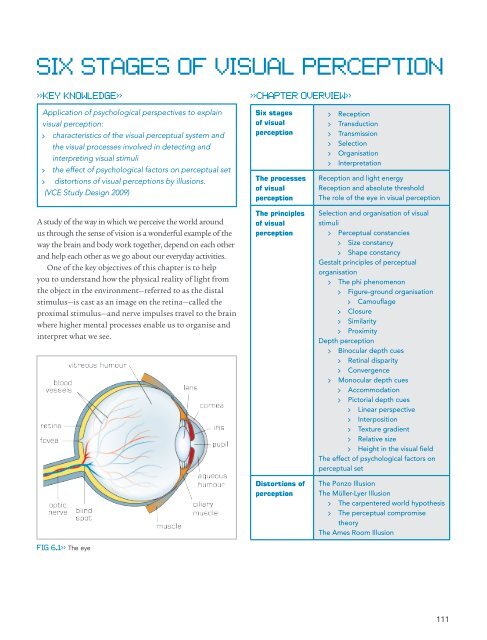
<strong>you</strong> to understand how the physical reality of light from<br />
the object in the environment—referred to as the distal<br />
stimulus—is cast as an image on the retina—called the<br />
proximal stimulus—and nerve impulses travel to the brain<br />
where higher mental processes enable us to organise and<br />
interpret what we see.<br />
fig 6.1>> The eye<br />
>>chapter overview>><br />
Six stages<br />
of visual<br />
perception<br />
The processes<br />
of visual<br />
perception<br />
The principles<br />
of visual<br />
perception<br />
Distortions of<br />
perception<br />
> Reception<br />
> Transduction<br />
> Transmission<br />
> Selection<br />
> Organisation<br />
> Interpretation<br />
Reception and light energy<br />
Reception and absolute threshold<br />
The role of the eye in visual perception<br />
Selection and organisation of visual<br />
stimuli<br />
> Perceptual constancies<br />
> Size constancy<br />
> Shape constancy<br />
Gestalt principles of perceptual<br />
organisation<br />
> The phi phenomenon<br />
> Figure-ground organisation<br />
> Camouflage<br />
> Closure<br />
> Similarity<br />
> Proximity<br />
Depth perception<br />
> Binocular depth cues<br />
> Retinal disparity<br />
> Convergence<br />
> Monocular depth cues<br />
> Accommodation<br />
> Pictorial depth cues<br />
> Linear perspective<br />
> Interposition<br />
> Texture gradient<br />
> Relative size<br />
> Height in the visual field<br />
The effect of psychological factors on<br />
perceptual set<br />
The Ponzo Illusion<br />
The Müller-Lyer Illusion<br />
> The carpentered world hypothesis<br />
> The perceptual compromise<br />
theory<br />
The Ames Room Illusion<br />
111