Quadratics - the Australian Mathematical Sciences Institute
Quadratics - the Australian Mathematical Sciences Institute
Quadratics - the Australian Mathematical Sciences Institute
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
{8} • <strong>Quadratics</strong><br />
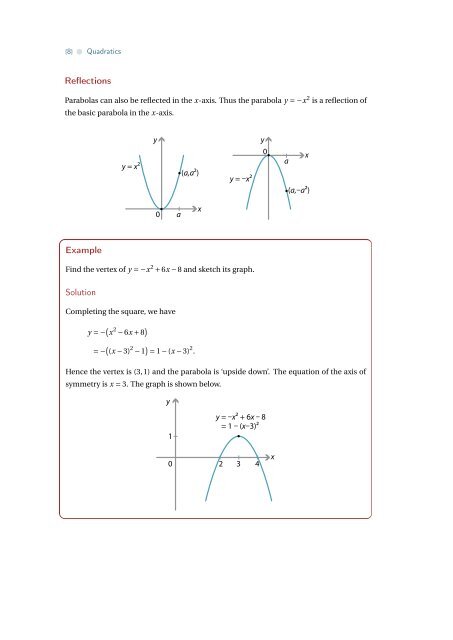
Reflections<br />
Parabolas can also be reflected in <strong>the</strong> x-axis. Thus <strong>the</strong> parabola y = −x 2 is a reflection of<br />
<strong>the</strong> basic parabola in <strong>the</strong> x-axis.<br />
y<br />
y<br />
y = x2<br />
(a,a2)<br />
y = –x2<br />
0<br />
a<br />
x<br />
(a,–a2)<br />
0 a<br />
x<br />
Example<br />
Find <strong>the</strong> vertex of y = −x 2 + 6x − 8 and sketch its graph.<br />
Solution<br />
Completing <strong>the</strong> square, we have<br />
y = − ( x 2 − 6x + 8 )<br />
= − ( (x − 3) 2 − 1 ) = 1 − (x − 3) 2 .<br />
Hence <strong>the</strong> vertex is (3,1) and <strong>the</strong> parabola is ‘upside down’. The equation of <strong>the</strong> axis of<br />
symmetry is x = 3. The graph is shown below.<br />
y<br />
1<br />
y = –x2 + 6x – 8<br />
= 1 – (x–3)2<br />
0<br />
2<br />
3 4<br />
x