Resilience in aquatic ecosystems - hysteresis, homeostasis, and ...
Resilience in aquatic ecosystems - hysteresis, homeostasis, and ...
Resilience in aquatic ecosystems - hysteresis, homeostasis, and ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Reynolds/Aquatic Ecosystem Health <strong>and</strong> Management 5 (2002) 3–17 13<br />
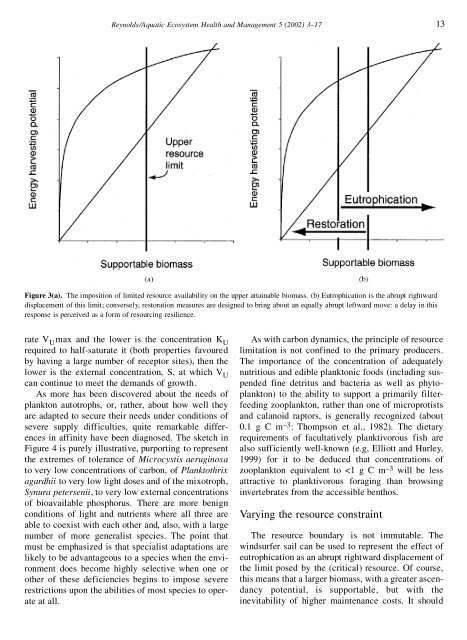
Figure 3(a). The imposition of limited resource availability on the upper atta<strong>in</strong>able biomass. (b) Eutrophication is the abrupt rightward<br />
displacement of this limit; conversely, restoration measures are designed to br<strong>in</strong>g about an equally abrupt leftward move: a delay <strong>in</strong> this<br />
response is perceived as a form of resourc<strong>in</strong>g resilience.<br />
rate V U max <strong>and</strong> the lower is the concentration K U<br />
required to half-saturate it (both properties favoured<br />
by hav<strong>in</strong>g a large number of receptor sites), then the<br />
lower is the external concentration, S, at which V U<br />
can cont<strong>in</strong>ue to meet the dem<strong>and</strong>s of growth.<br />
As more has been discovered about the needs of<br />
plankton autotrophs, or, rather, about how well they<br />
are adapted to secure their needs under conditions of<br />
severe supply difficulties, quite remarkable differences<br />
<strong>in</strong> aff<strong>in</strong>ity have been diagnosed. The sketch <strong>in</strong><br />
Figure 4 is purely illustrative, purport<strong>in</strong>g to represent<br />
the extremes of tolerance of Microcystis aerug<strong>in</strong>osa<br />
to very low concentrations of carbon, of Planktothrix<br />
agardhii to very low light doses <strong>and</strong> of the mixotroph,<br />
Synura petersenii, to very low external concentrations<br />
of bioavailable phosphorus. There are more benign<br />
conditions of light <strong>and</strong> nutrients where all three are<br />
able to coexist with each other <strong>and</strong>, also, with a large<br />
number of more generalist species. The po<strong>in</strong>t that<br />
must be emphasized is that specialist adaptations are<br />
likely to be advantageous to a species when the environment<br />
does become highly selective when one or<br />
other of these deficiencies beg<strong>in</strong>s to impose severe<br />
restrictions upon the abilities of most species to operate<br />
at all.<br />
As with carbon dynamics, the pr<strong>in</strong>ciple of resource<br />
limitation is not conf<strong>in</strong>ed to the primary producers.<br />
The importance of the concentration of adequately<br />
nutritious <strong>and</strong> edible planktonic foods (<strong>in</strong>clud<strong>in</strong>g suspended<br />
f<strong>in</strong>e detritus <strong>and</strong> bacteria as well as phytoplankton)<br />
to the ability to support a primarily filterfeed<strong>in</strong>g<br />
zooplankton, rather than one of microprotists<br />
<strong>and</strong> calanoid raptors, is generally recognized (about<br />
0.1 g C m –3 : Thompson et al., 1982). The dietary<br />
requirements of facultatively planktivorous fish are<br />
also sufficiently well-known (e.g, Elliott <strong>and</strong> Hurley,<br />
1999) for it to be deduced that concentrations of<br />
zooplankton equivalent to