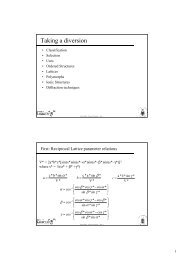
ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Wits Structural Chemistry
ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Wits Structural Chemistry
ELECTROCHEMISTRY - Wits Structural Chemistry
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
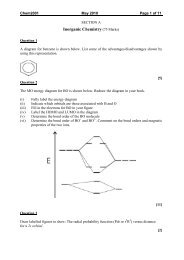
Example 3<br />
Devise a cell in which the cell reaction is:<br />
Mn(s) + Cl 2 (g) → MnCl 2 (aq)<br />
Give the half reactions at the electrodes and from the standard cell potential of 2.54 V<br />
deduce the standard potential for the Mn 2+ /Mn(s) redox couple.<br />
Given: E°(Cl 2 /Cl - ) = +1.36 V<br />
Example 4<br />
Estimate the cell potential at 25°C for<br />
Ag(s)|AgBr(s)|KBr(aq, 0.050 mol kg –1 )||Cd(NO 3 ) 2 (aq,0.0034 mol kg –1 )|Cd(s)<br />
E°(R-H) = –0.40 V E°(L-H) = +0.07 V (assume non-ideal solutions)<br />
Write the spontaneous electrochemical reaction.<br />
Example 5<br />
The standard potential of the cell below at 25 °C is 0.95 V.<br />
Ag(s) |AgI(s) | AgI(aq) | Ag(s)<br />
Calculate: a) its solubility constant and b) the solubility of AgI .<br />
MOLECULAR MOTION IN LIQUIDS<br />
Mass Transport<br />
Migration of ions - Conductivities of Electrolyte Solutions<br />
Mobilities of Ions<br />
Diffusion of Ions<br />
Part of Chapter 20<br />
Mass Transport<br />
Three main ways to transport ions to the surface of an electrode<br />
→ called mass transport<br />
Conductivities of Electrolyte Solutions<br />
Ions can be dragged through the solvent by applying a potential difference<br />
between two electrodes in solution.<br />
MIGRATION<br />
To measure conductivity:<br />
Incorporate conductivity cell into<br />
one arm of resistance bridge and<br />
search for balance point.<br />
R 3<br />
Convection<br />
Movement due to<br />
mechanical intervention.<br />
e.g. stirring, pumping,<br />
shaking<br />
Affects molecules and<br />
ions in solution.<br />
Diffusion<br />
Movement due to<br />
concentration gradient.<br />
e.g. movement across a<br />
cell membrane<br />
Affects molecules and<br />
ions in solution.<br />
Migration<br />
Movement due to applied<br />
electric field.<br />
e.g. in an electrolysis cell<br />
Affects only ions in<br />
solution.<br />
1 <br />
R =<br />
κ A<br />
1 <br />
κ =<br />
R A<br />
C<br />
κ =<br />
R<br />
R = resistance of solution (Ω)<br />
κ = conductivity (S cm -1 )<br />
= distance between electrodes<br />
A = area of electrodes<br />
C = cell constant<br />
κ depends on the number of ions in a solution.<br />
R 4<br />
2<br />
R 1<br />
R R =<br />
1 2<br />
R R<br />
3<br />
R 4<br />
Resistance bridge R 1R<br />
= R R3<br />
4 2<br />
Note: use ac current (ν~1kHz)<br />
to avoid electrolysis and<br />
polarisation of the electrodes<br />
which would change the<br />
composition of the solution at<br />
the electrode surfaces.<br />
4