- Page 2 and 3:
Diving Medicine for Scuba Divers 4t
- Page 4 and 5:
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ! For the 1 st and
- Page 6 and 7:
Chapter 1 All chapters, full text,
- Page 8 and 9:
The development of self-contained a
- Page 10 and 11:
Chapter 2 All chapters, full text,
- Page 12 and 13:
Water is much denser than air and 1
- Page 14 and 15:
This law can easily be demonstrated
- Page 16 and 17:
For example, if diver has a maximum
- Page 18 and 19:
Stated in another way; if a gas is
- Page 20 and 21:
Henry's Law This law describes the
- Page 22 and 23:
O 2 supports combustion vigorously
- Page 24 and 25:
BUOYANCY It is important for divers
- Page 26 and 27:
the water temperature decreases wit
- Page 28 and 29:
Chapter 3 All chapters, full text,
- Page 30 and 31:
Below the larynx the air passes thr
- Page 32 and 33:
Gas Uptake and Loss Air, which cont
- Page 34 and 35:
In venous blood, the haemoglobin in
- Page 36 and 37:
Circulation The blood flow from the
- Page 38 and 39:
educes the safety margin in the eve
- Page 40 and 41:
infections, hypothermia, panic and
- Page 42 and 43:
BREAK POINT Fig 4.2 . . This diagra
- Page 44 and 45:
MEDICAL CHECKLIST FOR SNORKELLERS H
- Page 46 and 47:
Some face masks are fitted with a o
- Page 48 and 49:
Snorkel The snorkel allows the dive
- Page 50 and 51:
A poorly fitting wet suit can cause
- Page 52 and 53:
entanglement with other equipment i
- Page 54 and 55:
1. Air supply, cylinder, tank 2. On
- Page 56 and 57:
Difficulties are still encountered
- Page 58 and 59:
STANDARD DRESS or HARD HAT This tra
- Page 60 and 61: Closed and Semi-closed Circuit REBR
- Page 62 and 63: the B.C. to be inflated using air f
- Page 64 and 65: The scuba tank may be negatively bu
- Page 66 and 67: Diving Watch A reliable, accurate,
- Page 68 and 69: Surface detection aids include: •
- Page 70 and 71: The "Half Tank Rule". The best tech
- Page 72 and 73: It is important to return to the su
- Page 74 and 75: The problems centre on impaired vis
- Page 76 and 77: The lower surface pressure also mea
- Page 78 and 79: In general, successful military div
- Page 80 and 81: Factors which upset a diver's emoti
- Page 82 and 83: The above story illustrates some of
- Page 84 and 85: Women divers must be doing somethin
- Page 86 and 87: convenience, most women today prefe
- Page 88 and 89: Other Diving Diseases In a number o
- Page 90 and 91: ! Decompression sickness. As mentio
- Page 92 and 93: Chapter 9 All chapters, full text,
- Page 94 and 95: vibrate. These vibrations are trans
- Page 96 and 97: Fig. 9.5 If equalisation does not o
- Page 98 and 99: If the ear drum was perforated, com
- Page 100 and 101: The diver should then equalise ever
- Page 102 and 103: If reasonable, avoid the use of hoo
- Page 104 and 105: One or more of these must be presen
- Page 106 and 107: There are four main groups of sinus
- Page 108 and 109: TREATMENT Any case of suspected sin
- Page 112 and 113: Fig. 11.2 The various clinical mani
- Page 114 and 115: Fig 11.3 The location of the medias
- Page 116 and 117: Occasionally a valve effect allows
- Page 118 and 119: The air bubbles obstruct or damage
- Page 120 and 121: Predisposing Factors ! Breath-holdi
- Page 122 and 123: In many navies free ascent training
- Page 124 and 125: ! Out of Air (OOA) and Low on Air (
- Page 126 and 127: PULMONARY BAROTRAUMA OF DESCENT (LU
- Page 128 and 129: This condition is easily prevented
- Page 130 and 131: SUIT BAROTRAUMA OF ASCENT ("BLOW UP
- Page 132 and 133: Chapter 13 All chapters, full text,
- Page 134 and 135: SATURATION When tissues are subject
- Page 136 and 137: DIVE PROFILES The type of dive has
- Page 138 and 139: ! Cold. Diving in cold conditions m
- Page 140 and 141: A very short surface interval may a
- Page 142 and 143: ased on modified Haldane principles
- Page 144 and 145: DECOMPRESSION METERS and COMPUTERS
- Page 146 and 147: ! Safety suggestions (the DC Ten Co
- Page 148 and 149: ONSET OF SYMPTOMS The clinical feat
- Page 150 and 151: confined within the solid bone of t
- Page 152 and 153: SKIN MANIFESTATIONS of DCS These ar
- Page 154 and 155: The ABBREVIATED MENTAL TEST SCORE (
- Page 156 and 157: Unfortunately 100% O 2 can be toxic
- Page 158 and 159: Transportation in aircraft presents
- Page 160 and 161:
Other tables are available which in
- Page 162 and 163:
! Slow ascent rates. A slow ascent
- Page 164 and 165:
epeated minor trauma which is commo
- Page 166 and 167:
Prevention Avoidance of the known p
- Page 168 and 169:
CAUSES OF NITROGEN NARCOSIS The exa
- Page 170 and 171:
A diver who can "hold his liquor" i
- Page 172 and 173:
CLINICAL FEATURES The first sign is
- Page 174 and 175:
obstruction somewhere in the respir
- Page 176 and 177:
the lungs and body into the counter
- Page 178 and 179:
Chapter 21 All chapters, full text,
- Page 180 and 181:
CAUSES OF O 2 TOXICITY For resuscit
- Page 182 and 183:
Pulmonary Effects These effects wil
- Page 184 and 185:
Clinical Features A person hyperven
- Page 186 and 187:
CO 2 toxicity may increase the like
- Page 188 and 189:
CLINICAL FEATURES Symptoms are thos
- Page 190 and 191:
Chapter 24 All chapters, full text,
- Page 192 and 193:
If the compressor is operated in an
- Page 194 and 195:
Chapter 25 All chapters, full text,
- Page 196 and 197:
eaches the surface. If the diver is
- Page 198 and 199:
TREATMENT Rescue and recovery from
- Page 200 and 201:
PREVENTION It is paradoxical that d
- Page 202 and 203:
Chapter 26 All chapters, full text,
- Page 204 and 205:
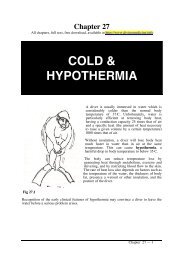
Chapter 27 All chapters, full text,
- Page 206 and 207:
Fig. 27.3 Graph illustrating surviv
- Page 208 and 209:
PREVENTION Alcohol and other drugs
- Page 210 and 211:
Occasionally this disorder has been
- Page 212 and 213:
! Treatment. All coral cuts should
- Page 214 and 215:
! Vibrio and other Aquatic Organism
- Page 216 and 217:
SWIMMING POOL GRANULOMA Also called
- Page 218 and 219:
Until the risk is excluded it would
- Page 220 and 221:
MARINE Chapter 29 All chapters, ful
- Page 222 and 223:
! Stop the blood loss. This must be
- Page 224 and 225:
The venom has its most serious effe
- Page 226 and 227:
IRUKANDJI SYNDROME This disorder wa
- Page 228 and 229:
The first aid basic life support me
- Page 230 and 231:
hospital as soon as possible. Serio
- Page 232 and 233:
The spine may produce a puncture an
- Page 234 and 235:
Chapter 30 All chapters, full text,
- Page 236 and 237:
Middle Ear Disorders Disturbances o
- Page 238 and 239:
Chapter 31 All chapters, full text,
- Page 240 and 241:
CAUSES OF VERTIGO Problems arising
- Page 242 and 243:
Nitrogen narcosis may aggravate ver
- Page 244 and 245:
CRAMPS Cramp is a painful spasm of
- Page 246 and 247:
Air emboli and bubble development i
- Page 248 and 249:
Cold water entering an ear canal ca
- Page 250 and 251:
unconsciousness have been well reco
- Page 252 and 253:
SEASICKNESS This is a distressing a
- Page 254 and 255:
EXPLOSIONS - UNDERWATER BLAST This
- Page 256 and 257:
In addition to these the causes ass
- Page 258 and 259:
COLD OR HYPOTHERMIA (SEE CHAPTERS 3
- Page 260 and 261:
GENERAL MEDICAL CONDITIONS A variet
- Page 262 and 263:
Chapter 34 All chapters, full text,
- Page 264 and 265:
! Major Causes of Death identified
- Page 266 and 267:
unfortunately promoted by some inst
- Page 268 and 269:
Fig 34.3 But not always ! Buddy res
- Page 270 and 271:
Salt Water Aspiration This factor w
- Page 272 and 273:
Nitrogen Narcosis This was an effec
- Page 274 and 275:
Other Equipment Problems In 5% or l
- Page 276 and 277:
SUMMARY Diving fatalities generally
- Page 278 and 279:
Chapter 35 All chapters, full text,
- Page 280 and 281:
CONTRIBUTING CAUSES There are a num
- Page 282 and 283:
This reflex is present to some exte
- Page 284 and 285:
! Myocarditis. Some viral infection
- Page 286 and 287:
Flora Fisk Quiz for Recreational Di
- Page 288 and 289:
(50 ft) and admitted to being "bent
- Page 290 and 291:
is undertaken. Then a drug reaction
- Page 292 and 293:
Antihistamines These are usually ta
- Page 294 and 295:
PROPHYLACTIC (PREVENTION) DRUGS Sta
- Page 296 and 297:
Marijuana — Cannabis or "pot" Chr
- Page 298 and 299:
Chapter 38 All chapters, full text,
- Page 300 and 301:
Some antibiotics may have no direct
- Page 302 and 303:
The hearing function test (pure ton
- Page 304 and 305:
MEDICAL EXAMINATION FORMAT There is
- Page 306 and 307:
Chapter 38 — 9
- Page 308 and 309:
Chapter 38 — 11
- Page 310 and 311:
RESUSCITATION EQUIPMENT • Airways
- Page 312 and 313:
INFORMATION NEEDED about a DIVING A
- Page 314 and 315:
in medicine have 100% O 2 delivered
- Page 316 and 317:
compatible. Otherwise the diving il
- Page 318 and 319:
GENERAL INFORMATION Oxygen Toxicity
- Page 320 and 321:
Chapter 41 All chapters, full text,
- Page 322 and 323:
CHECK LIST FOR DIVING ACCIDENTS INF
- Page 324 and 325:
D and R - DANGER and RESPONSE DANGE
- Page 326 and 327:
If the rescuer has the equipment an
- Page 328 and 329:
Duration of CPR Continue CPR until:
- Page 330 and 331:
Chapter 43 All chapters, full text,
- Page 332 and 333:
THE TECHNICAL DIVE 1. DIVE PROTOCOL
- Page 334 and 335:
For the same depth/duration dive, t
- Page 336 and 337:
OXYGEN ENRICHED AIR or NITROX (EANx
- Page 338 and 339:
likely to oxidise and have a higher
- Page 340 and 341:
There is also a greater conductive
- Page 342 and 343:
The carbon dioxide absorbent must b
- Page 344 and 345:
• The oxygen rebreathers are clos
- Page 346 and 347:
CONCLUSION There are few problems i
- Page 348 and 349:
The actual incidence is unknown, bu
- Page 350 and 351:
Appendix A All chapters, full text,
- Page 352 and 353:
DIVING MEDICAL TEXTS • *Diving Me
- Page 354 and 355:
Appendix B All chapters, full text,
- Page 356 and 357:
Appendix C All chapters, full text,
- Page 358 and 359:
Appendix D All chapters, full text,