Guidelines For Professional Working Standards Ultrasound Practice
Guidelines For Professional Working Standards Ultrasound Practice
Guidelines For Professional Working Standards Ultrasound Practice
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
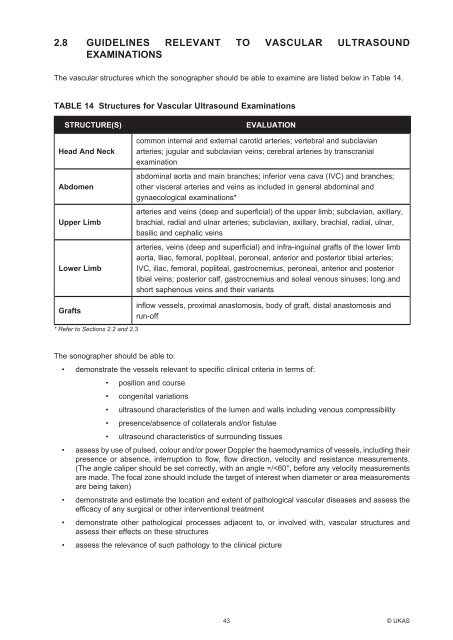
2.8 <strong>Guidelines</strong> Relevant To Vascular <strong>Ultrasound</strong><br />
Examinations<br />
The vascular structures which the sonographer should be able to examine are listed below in Table 14.<br />
TABLE 14 Structures for Vascular <strong>Ultrasound</strong> Examinations<br />
STRUCTURE(S)<br />
Head And Neck<br />
Abdomen<br />
Upper Limb<br />
Lower Limb<br />
EVALUATION<br />
common internal and external carotid arteries; vertebral and subclavian<br />
arteries; jugular and subclavian veins; cerebral arteries by transcranial<br />
examination<br />
abdominal aorta and main branches; inferior vena cava (IVC) and branches;<br />
other visceral arteries and veins as included in general abdominal and<br />
gynaecological examinations*<br />
arteries and veins (deep and superficial) of the upper limb; subclavian, axillary,<br />
brachial, radial and ulnar arteries; subclavian, axillary, brachial, radial, ulnar,<br />
basilic and cephalic veins<br />
arteries, veins (deep and superficial) and infra-inguinal grafts of the lower limb<br />
aorta, Iliac, femoral, popliteal, peroneal, anterior and posterior tibial arteries;<br />
IVC, iliac, femoral, popliteal, gastrocnemius, peroneal, anterior and posterior<br />
tibial veins; posterior calf, gastrocnemius and soleal venous sinuses; long and<br />
short saphenous veins and their variants<br />
Grafts<br />
* Refer to Sections 2.2 and 2.3<br />
inflow vessels, proximal anastomosis, body of graft, distal anastomosis and<br />
run-off<br />
The sonographer should be able to:<br />
• demonstrate the vessels relevant to specific clinical criteria in terms of:<br />
• position and course<br />
• congenital variations<br />
• ultrasound characteristics of the lumen and walls including venous compressibility<br />
• presence/absence of collaterals and/or fistulae<br />
• ultrasound characteristics of surrounding tissues<br />
• assess by use of pulsed, colour and/or power Doppler the haemodynamics of vessels, including their<br />
presence or absence, interruption to flow, flow direction, velocity and resistance measurements.<br />
(The angle caliper should be set correctly, with an angle =/