Enhancing China's Competitiveness Through Lifelong Learning ...
Enhancing China's Competitiveness Through Lifelong Learning ...
Enhancing China's Competitiveness Through Lifelong Learning ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Developing a System of <strong>Lifelong</strong> <strong>Learning</strong> for China and the New Role for Government 27<br />
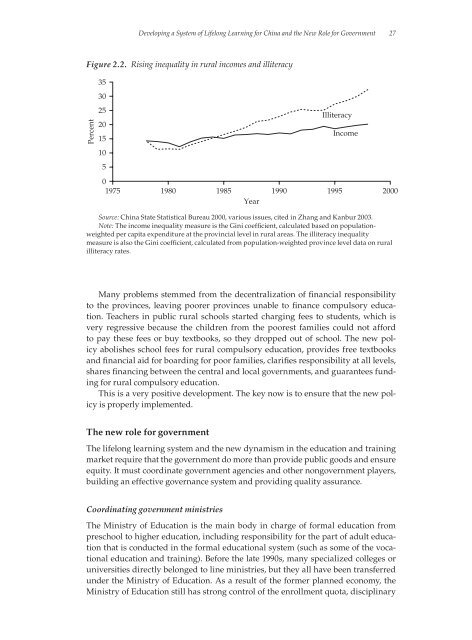
Figure 2.2. Rising inequality in rural incomes and illiteracy<br />
35<br />
30<br />
Percent<br />
25<br />
20<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
Illiteracy<br />
Income<br />
0<br />
1975<br />
1980<br />
1985<br />
Year<br />
1990<br />
1995<br />
2000<br />
Source: China State Statistical Bureau 2000, various issues, cited in Zhang and Kanbur 2003.<br />
Note: The income inequality measure is the Gini coefficient, calculated based on populationweighted<br />
per capita expenditure at the provincial level in rural areas. The illiteracy inequality<br />
measure is also the Gini coefficient, calculated from population-weighted province level data on rural<br />
illiteracy rates.<br />
Many problems stemmed from the decentralization of financial responsibility<br />
to the provinces, leaving poorer provinces unable to finance compulsory education.<br />
Teachers in public rural schools started charging fees to students, which is<br />
very regressive because the children from the poorest families could not afford<br />
to pay these fees or buy textbooks, so they dropped out of school. The new policy<br />
abolishes school fees for rural compulsory education, provides free textbooks<br />
and financial aid for boarding for poor families, clarifies responsibility at all levels,<br />
shares financing between the central and local governments, and guarantees funding<br />
for rural compulsory education.<br />
This is a very positive development. The key now is to ensure that the new policy<br />
is properly implemented.<br />
The new role for government<br />
The lifelong learning system and the new dynamism in the education and training<br />
market require that the government do more than provide public goods and ensure<br />
equity. It must coordinate government agencies and other nongovernment players,<br />
building an effective governance system and providing quality assurance.<br />
Coordinating government ministries<br />
The Ministry of Education is the main body in charge of formal education from<br />
preschool to higher education, including responsibility for the part of adult education<br />
that is conducted in the formal educational system (such as some of the vocational<br />
education and training). Before the late 1990s, many specialized colleges or<br />
universities directly belonged to line ministries, but they all have been transferred<br />
under the Ministry of Education. As a result of the former planned economy, the<br />
Ministry of Education still has strong control of the enrollment quota, disciplinary