Handbook of Magnetic Compass Adjustment - Maritime Safety ...
Handbook of Magnetic Compass Adjustment - Maritime Safety ...
Handbook of Magnetic Compass Adjustment - Maritime Safety ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
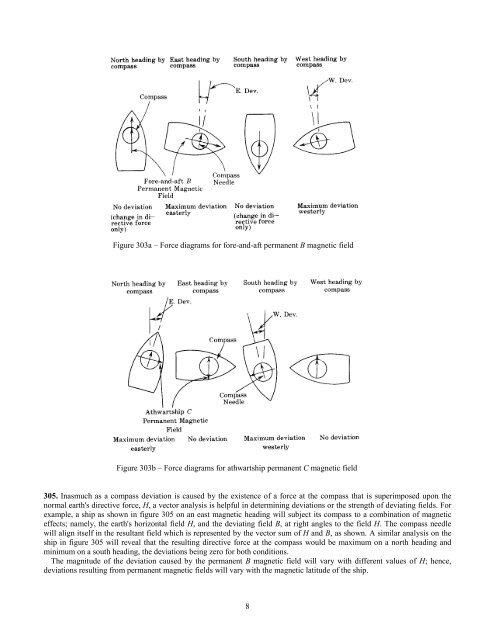
Figure 303a – Force diagrams for fore-and-aft permanent B magnetic field<br />
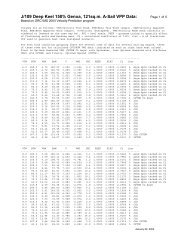
Figure 303b – Force diagrams for athwartship permanent C magnetic field<br />
305. Inasmuch as a compass deviation is caused by the existence <strong>of</strong> a force at the compass that is superimposed upon the<br />
normal earth's directive force, H, a vector analysis is helpful in determining deviations or the strength <strong>of</strong> deviating fields. For<br />
example, a ship as shown in figure 305 on an east magnetic heading will subject its compass to a combination <strong>of</strong> magnetic<br />
effects; namely, the earth's horizontal field H, and the deviating field B, at right angles to the field H. The compass needle<br />
will align itself in the resultant field which is represented by the vector sum <strong>of</strong> H and B, as shown. A similar analysis on the<br />
ship in figure 305 will reveal that the resulting directive force at the compass would be maximum on a north heading and<br />
minimum on a south heading, the deviations being zero for both conditions.<br />
The magnitude <strong>of</strong> the deviation caused by the permanent B magnetic field will vary with different values <strong>of</strong> H; hence,<br />
deviations resulting from permanent magnetic fields will vary with the magnetic latitude <strong>of</strong> the ship.<br />
8