Chapter 2 Introduction to Neural network
Chapter 2 Introduction to Neural network
Chapter 2 Introduction to Neural network
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
□<br />
A formula for R(m, n)<br />
∑n−1<br />
( ) m − 1<br />
R(m, n) = 2<br />
i<br />
i=0<br />
For a <strong>network</strong> with 3 hidden units with structure n−k −l −m that<br />
is, n input nodes k first hidden nodes, l second hidden nodes and<br />
m output nodes we get<br />
max # regions = min{R(k, n), R(l, k), R(m, l)}<br />
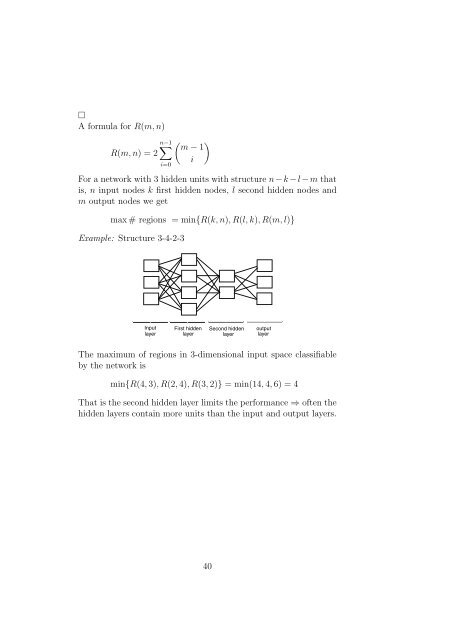
Example: Structure 3-4-2-3<br />
Input<br />
layer<br />
First hidden<br />
layer<br />
Second hidden<br />
layer<br />
output<br />
layer<br />
The maximum of regions in 3-dimensional input space classifiable<br />
by the <strong>network</strong> is<br />
min{R(4, 3), R(2, 4), R(3, 2)} = min(14, 4, 6) = 4<br />
That is the second hidden layer limits the performance ⇒ often the<br />
hidden layers contain more units than the input and output layers.<br />
40